A*寻路算法(Python)
 AI角色从起点开始,每一步只能向上、下、左、右移动1格,且不能穿越墙壁,那么如何让AI角色用最少的步数达到终点?
AI角色从起点开始,每一步只能向上、下、左、右移动1格,且不能穿越墙壁,那么如何让AI角色用最少的步数达到终点?
发布日期:2021-05-08 01:40:28
浏览次数:11
分类:精选文章
本文共 3783 字,大约阅读时间需要 12 分钟。
一、题目描述
在一个迷宫游戏里,有一些小怪物要去攻击主角,现在希望给这些小怪物加上聪明的AI,让他们可以自动绕过迷宫中的障碍物,寻找到主角所在。 二、解题思路 迷宫游戏里的场景通常都是由小方格组成。假设我们有一个7*5大小的迷宫,图中红色格子是终点,绿色格子是起点,蓝色格子是一堵墙。 AI角色从起点开始,每一步只能向上、下、左、右移动1格,且不能穿越墙壁,那么如何让AI角色用最少的步数达到终点?
AI角色从起点开始,每一步只能向上、下、左、右移动1格,且不能穿越墙壁,那么如何让AI角色用最少的步数达到终点? 首先要引入两个集合和1个公式:
open_list:可到达的格子 close_list:已到达的格子 一个公式如下: F=G+H 每一个格子都具有F、G、H这三个属性: G:从起点走到当前格子的成本,也就是已经花费了多少步。 H:在不考虑障碍的情况下,从当前格子走到目标格子的距离,也就是离目标还有多远。 F:G和H的综合评估,也就是从起点到达当前格子,再从当前格子到达目标格子的总步数。第一步:把起点放入open_list,也就是可到达格子的集合。
第二步:找出open_list中F值最小的方格作为当前方格。 第三步:找出当前方格上下左右所有可到达的格子,看他们是否在open_list或者close_list中,如果不在,则将他们加入open_list中。计算出相应G、H、F值,并把当前格子作为他们的父节点。 之后进行第二轮,我们需要一次又一次重复刚刚的第二不和第三步,直到直到终点为止。三、代码实现
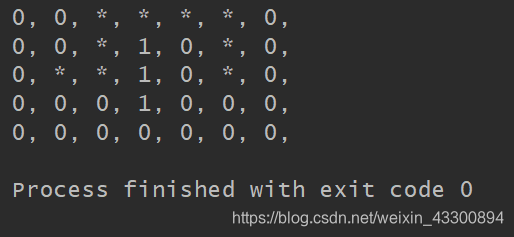
def a_star_search(start, end): # 待访问的格子 open_list = [] # 已访问的格子 close_list = [] # 把起点加入open_list open_list.append(start) # 主循环,每一轮检查一个当前方格节点 while len(open_list) > 0: # 在open_list中查找 F值最小的节点作为当前方格节点 current_grid = find_min_gird(open_list) # 当前方格节点从openList中移除 open_list.remove(current_grid) # 当前方格节点进入 closeList close_list.append(current_grid) # 找到所有邻近节点 neighbors = find_neighbors(current_grid, open_list, close_list) for grid in neighbors: if grid not in open_list: # 邻近节点不在openList中,标记父亲、G、H、F,并放入openList grid.init_grid(current_grid, end) open_list.append(grid) # 如果终点在openList中,直接返回终点格子 for grid in open_list: if (grid.x == end.x) and (grid.y == end.y): return grid # openList用尽,仍然找不到终点,说明终点不可到达,返回空 return Nonedef find_min_gird(open_list=[]): temp_grid = open_list[0] for grid in open_list: if grid.f < temp_grid.f: temp_grid = grid return temp_griddef find_neighbors(grid, open_list=[], close_list=[]): grid_list = [] if is_valid_grid(grid.x, grid.y-1, open_list, close_list): grid_list.append(Grid(grid.x, grid.y-1)) if is_valid_grid(grid.x, grid.y+1, open_list, close_list): grid_list.append(Grid(grid.x, grid.y+1)) if is_valid_grid(grid.x-1, grid.y, open_list, close_list): grid_list.append(Grid(grid.x-1, grid.y)) if is_valid_grid(grid.x+1, grid.y, open_list, close_list): grid_list.append(Grid(grid.x+1, grid.y)) return grid_listdef is_valid_grid(x, y, open_list=[], close_list=[]): # 是否超过边界 if x < 0 or x >= len(MAZE) or y < 0 or y >= len(MAZE[0]): return False # 是否有障碍物 if MAZE[x][y] == 1: return False # 是否已经在open_list中 if contain_grid(open_list, x, y): return False # 是否已经在closeList中 if contain_grid(close_list, x, y): return False return Truedef contain_grid(grids, x, y): for grid in grids: if (grid.x == x) and (grid.y == y): return True return Falseclass Grid: def __init__(self, x, y): self.x = x self.y = y self.f = 0 self.g = 0 self.h = 0 self.parent = None def init_grid(self, parent, end): self.parent = parent if parent is not None: self.g = parent.g + 1 else: self.g=1 self.h = abs(self.x - end.x) + abs(self.y - end.y) self.f = self.g + self.h# 迷宫地图MAZE = [ [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]# 设置起点和终点start_grid = Grid(2, 1)end_grid = Grid(2, 5)# 搜索迷宫终点result_grid = a_star_search(start_grid, end_grid)# 回溯迷宫路径path = []while result_grid is not None: path.append(Grid(result_grid.x, result_grid.y)) result_grid = result_grid.parent# 输出迷宫和路径,路径用星号表示for i in range(0, len(MAZE)): for j in range(0, len(MAZE[0])): if contain_grid(path, i, j): print("*, ", end='') else: print(str(MAZE[i][j]) + ", ", end='') print() 发表评论
最新留言
留言是一种美德,欢迎回访!
[***.207.175.100]2025年03月22日 09时35分19秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
Vue实现选项卡功能
2021-05-07
数据结构——链表
2021-05-07
[编程题]Course List for Student (25)
2021-05-07
【Python】面向对象,封装
2021-05-07
接口又是个啥?
2021-05-07
5.11 TEST1
2021-05-07
uni-app请求头中携带token
2021-05-07
常用的 Git 命令和小技巧(1)
2021-05-07
vue中接收后台的图片验证码并显示
2021-05-07
springboot入门(1)---整合MyBatis
2021-05-07
Vue入门学习笔记(1)
2021-05-07
ECharts——双向柱状图
2021-05-07
Vue——引进bootstrap
2021-05-07
Vue——引进ivew
2021-05-07
趣谈win10常用快捷键
2021-05-07
数学建模(NO.18灰色预测)
2021-05-07
数学建模更新12(数学线性规划模型1)
2021-05-07
Android,SharedPreferences的使用
2021-05-07
华为hybrid vlan配置
2021-05-07