
设计模式之享元模式
发布日期:2021-05-07 15:14:44
浏览次数:12
分类:原创文章
本文共 2572 字,大约阅读时间需要 8 分钟。
目录
享元模式flyweight
概念
- Flyweight模式也叫享元模式,是构造型模式之一,它通过与其他类似对象共享数据来减小内存占用。
- 在面向对象系统的设计何实现中,创建对象是最为常见的操作。
- 这里面就有一个问题:
- 如果一个应用程序使用了太多的对象,就会造成很大的存储开销。
- 特别是对于大量轻量级(细粒度)的对象,比如在文档编辑器的设计过程中,我们如果为没有字母创建一个对象的话,系统可能会因为大量的对象而造成存储开销的浪费。
- 例如一个字母"a"在文档中出现了100000次,而实际上我们可以让这一万个字母"a"共享一个对象
- 当然因为在不同的位置可能字母"a"有不同的显示效果(例如字体和大小等设置不同),在这种情况我们可以为将对象的状态分为“外部状态”和“内部状态”,将可以被共享(不会变化)的状态作为内部状态存储在对象中,而外部对象(例如上面提到的字体、大小等)我们可以在适当的时候将外部对象最为参数传递给对象(例如在显示的时候,将字体、大小等信息传递给对象)。
角色和职责
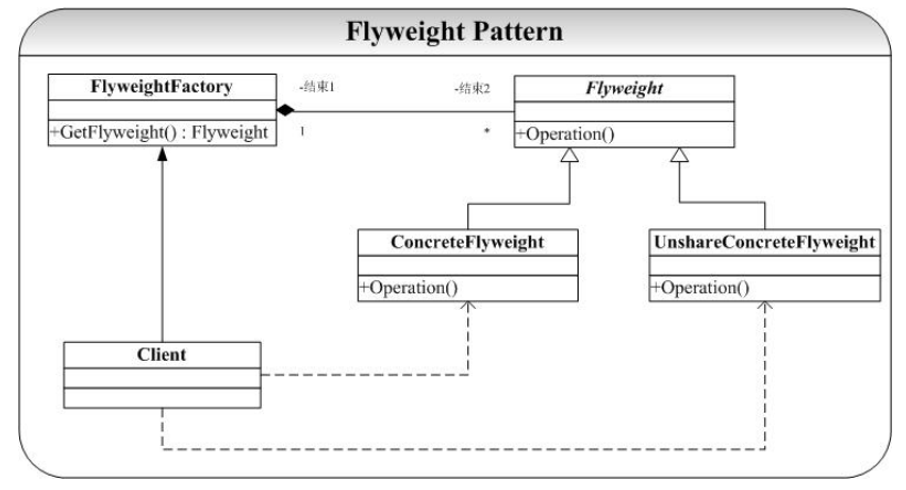
- 抽象享元角色:
- 所有具体享元类的父类,规定一些需要实现的公共接口。
- 具体享元角色:
- 抽象享元角色的具体实现类,并实现了抽象享元角色规定的方法。
- 享元工厂角色:
- 负责创建和管理享元角色。
- 使用场景:
- 是以共享的方式,高效的支持大量的细粒度的对象
案例
class Person{public: Person(string name, int age, int sex) { this->name = name; this->age = age; this->sex = sex; } string getName() { return name; } int getAge() { return age; } int getSex() { return sex; }protected: string name; int age; int sex; //1男 2女};class Teacher : public Person{public: Teacher(string id, string name, int age, int sex) : Person(name, age, sex) { this->id = id; } string getId() { return id; } void printT() { cout << "id:" <<id << "\t" << "name:" <<name << "\t" << "age:" <<age << "\t" << "sex:" <<sex << "\t" << endl; }private: string id;};class TeacherFactory{public: TeacherFactory() { m_tpool.empty(); } ~TeacherFactory() { //内存管理 永远是c++程序员的痛 while (!m_tpool.empty()) //在工厂中创建老师结点,在工厂中销毁老师结点 { Teacher *tmp = NULL; map<string, Teacher *>::iterator it = m_tpool.begin(); tmp = it->second; m_tpool.erase(it); delete tmp; } } //通过Teacher的pool,来存放老师结点,在TeacherFactory中创建老师、销毁老师 Teacher *getTeacher(string tid) { string name; int age; int sex; Teacher *tmp = NULL; map<string, Teacher*>::iterator it = m_tpool.find(tid); if (it == m_tpool.end()) { cout << "id为: " << tid << " 的老师不存在,系统为你创建该老师,请输入以下信息" <<endl; cout << "请输入老师姓名:"; cin >> name; cout << "请输入老师年龄:"; cin >> age; cout << "请输入老师性别 1男 2女:"; cin >> sex; tmp = new Teacher(tid, name, age, sex); m_tpool.insert(pair<string, Teacher*>(tid, tmp)); } else { tmp = (it->second); } return tmp; }private: map<string, Teacher *> m_tpool;};void main(){ /* Teacher *t1 = new Teacher("001", "小李", 30, 1); Teacher *t2 = new Teacher("002", "小张", 30, 1); Teacher *t3 = new Teacher("001", "小李", 30, 1); Teacher *t4 = new Teacher("004", "小吴", 30, 1); // cout << "t1 t3的 工号一样,但是也不是同一个人 " << endl; delete t1; delete t2; delete t3; delete t4; */ TeacherFactory *teacherFactory = new TeacherFactory; Teacher *t1 = teacherFactory->getTeacher("001"); t1->printT(); Teacher *t2 = teacherFactory->getTeacher("001"); t2->printT(); delete teacherFactory; system("pause"); return ;}
发表评论
最新留言
表示我来过!
[***.240.166.169]2025年03月25日 08时59分54秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
软件架构-zookeeper快速入门
2019-03-04
软件架构-zookeeper场景和实现
2019-03-04
「初级篇」跟我一起学docker(四)--容器的基本操作
2019-03-04
22 岁毕业做程序员的「普通」人,50 岁时的人生轨迹是怎样的?
2019-03-04
『高级篇』docker之安全认证kubernetes命令熟悉(40)
2019-03-04
scala上界与下界、协变与逆变
2019-03-04
java稀疏数组
2019-03-04
全球数字货币加快研发
2019-03-04
数字化助力金融科技,实现产业良性循环
2019-03-04
2020-11-23(彻底理解KMP)
2019-03-04
常用的IDC函数
2019-03-04
BUUCTF 新年快乐 内涵的软件 Java逆向解密 刮开有奖
2019-03-04
angr学习笔记(7)(malloc地址单元符号化)
2019-03-04
angr学习笔记(9)(添加约束)
2019-03-04
angr学习笔记(13)(static_binary)
2019-03-04
windows环境利用start命令实现微信多开
2019-03-04
「CF149D」括号涂色 区间DP好题
2019-03-04
树状数组 模板总结
2019-03-04
「NOI2015」程序自动分析 并查集题解
2019-03-04
[JSOI2008]Blue Mary的战役地图 Hash题解
2019-03-04