
自然语言处理实例
发布日期:2021-07-01 02:13:12
浏览次数:2
分类:技术文章
本文共 12346 字,大约阅读时间需要 41 分钟。
自然语言处理实例
数据简介: Disasters on social media
社交媒体上有些讨论是关于灾难,疾病,暴乱的,有些只是开玩笑或者是电影情节,我们该如何让机器能分辨出这两种讨论呢?
import kerasimport nltkimport pandas as pdimport numpy as npimport reimport codecs
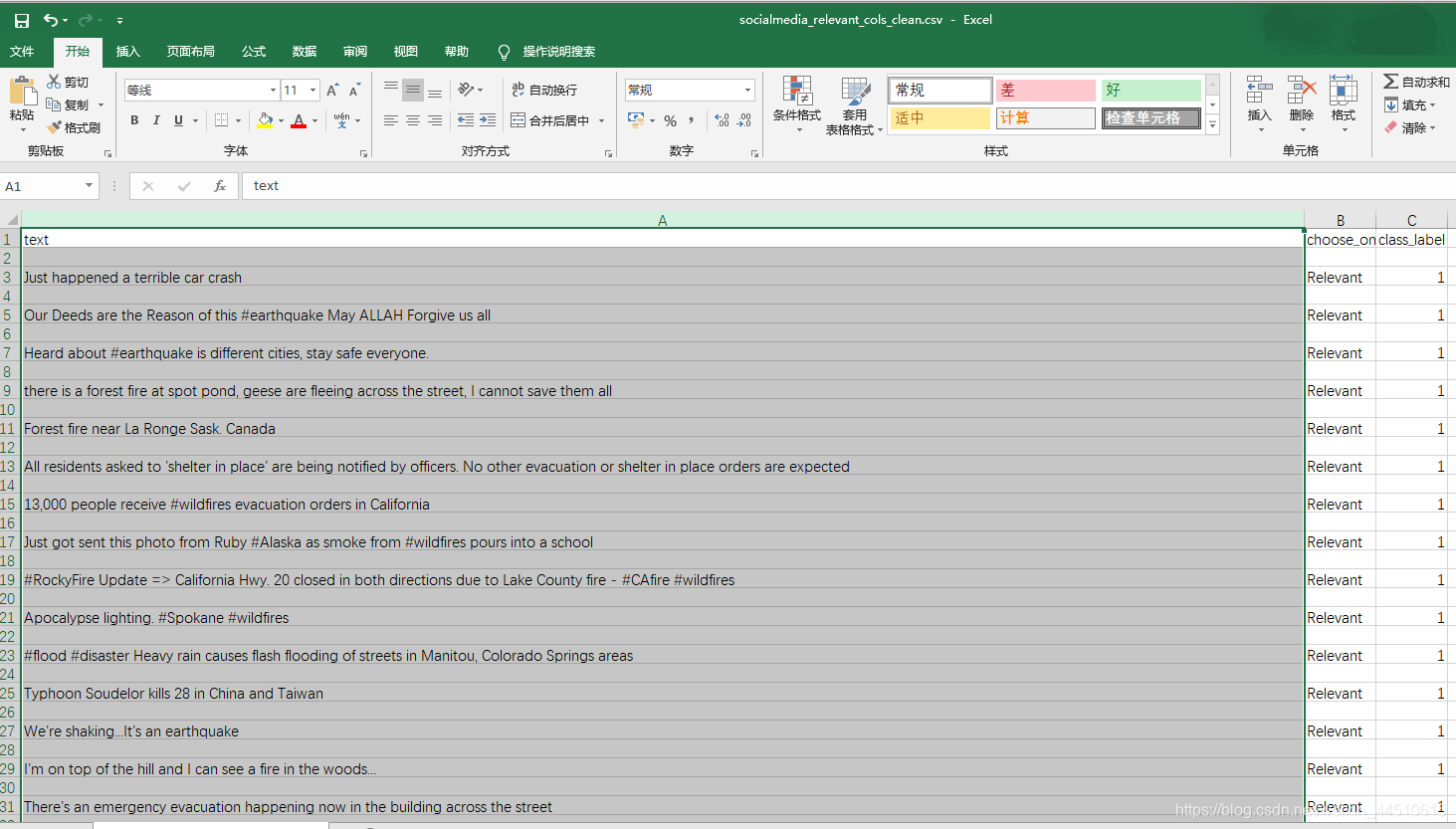
questions = pd.read_csv("socialmedia_relevant_cols_clean.csv")questions.columns=['text', 'choose_one', 'class_label']questions.head() | text | choose_one | class_label | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Just happened a terrible car crash | Relevant | 1 |
| 1 | Our Deeds are the Reason of this #earthquake M... | Relevant | 1 |
| 2 | Heard about #earthquake is different cities, s... | Relevant | 1 |
| 3 | there is a forest fire at spot pond, geese are... | Relevant | 1 |
| 4 | Forest fire near La Ronge Sask. Canada | Relevant | 1 |
questions.describe()
| class_label | |
|---|---|
| count | 10876.000000 |
| mean | 0.432604 |
| std | 0.498420 |
| min | 0.000000 |
| 25% | 0.000000 |
| 50% | 0.000000 |
| 75% | 1.000000 |
| max | 2.000000 |
数据清洗,去掉无用字符
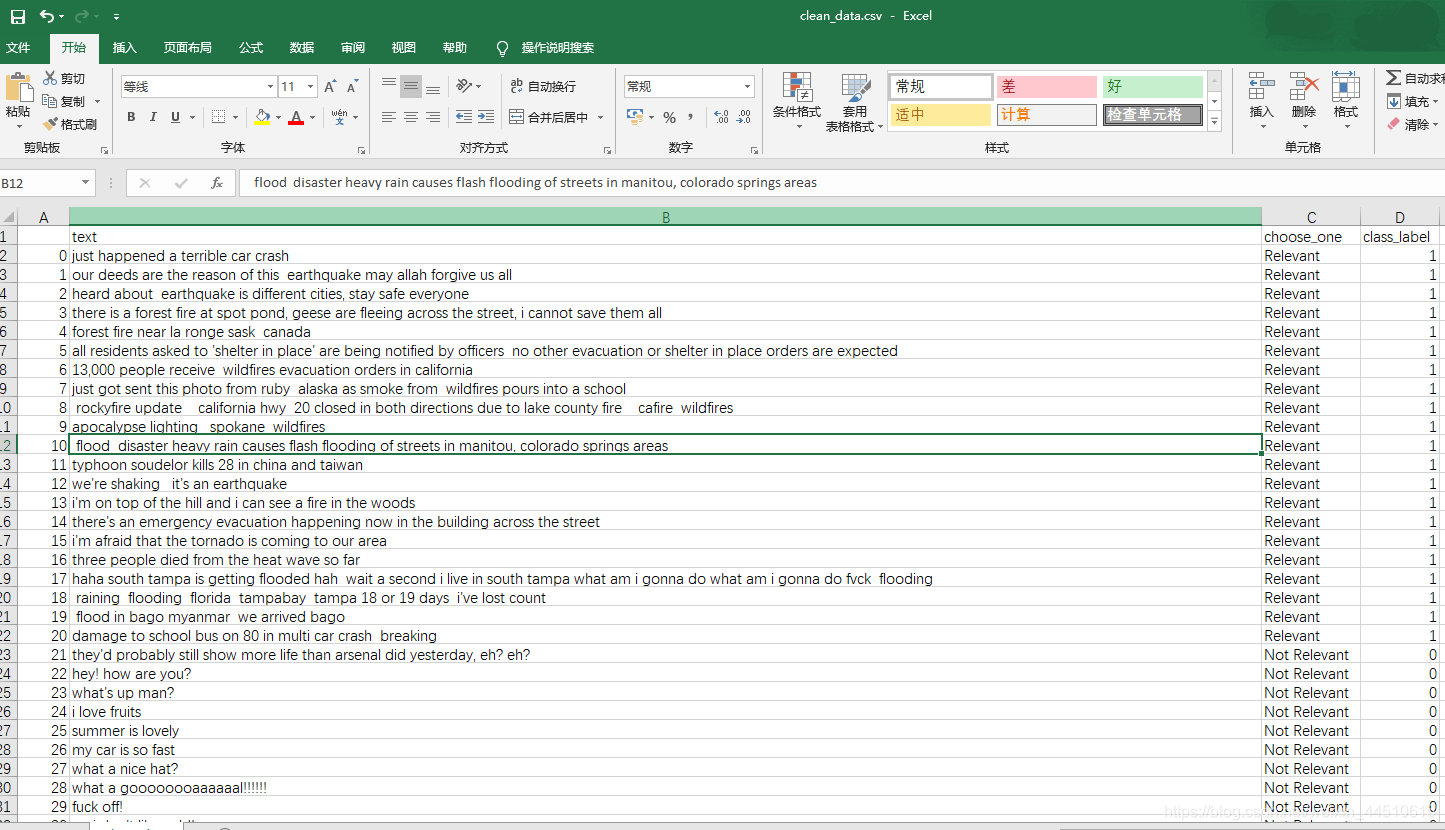
def standardize_text(df, text_field): df[text_field] = df[text_field].str.replace(r"http\S+", "") df[text_field] = df[text_field].str.replace(r"http", "") df[text_field] = df[text_field].str.replace(r"@\S+", "") df[text_field] = df[text_field].str.replace(r"[^A-Za-z0-9(),!?@\'\`\"\_\n]", " ") df[text_field] = df[text_field].str.replace(r"@", "at") df[text_field] = df[text_field].str.lower() return dfquestions = standardize_text(questions, "text")questions.to_csv("clean_data.csv")questions.head() | text | choose_one | class_label | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | just happened a terrible car crash | Relevant | 1 |
| 1 | our deeds are the reason of this earthquake m... | Relevant | 1 |
| 2 | heard about earthquake is different cities, s... | Relevant | 1 |
| 3 | there is a forest fire at spot pond, geese are... | Relevant | 1 |
| 4 | forest fire near la ronge sask canada | Relevant | 1 |
clean_questions = pd.read_csv("clean_data.csv")clean_questions.tail() | Unnamed: 0 | text | choose_one | class_label | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10871 | 10871 | m1 94 01 04 utc ?5km s of volcano hawaii | Relevant | 1 |
| 10872 | 10872 | police investigating after an e bike collided ... | Relevant | 1 |
| 10873 | 10873 | the latest more homes razed by northern calif... | Relevant | 1 |
| 10874 | 10874 | meg issues hazardous weather outlook (hwo) | Relevant | 1 |
| 10875 | 10875 | cityofcalgary has activated its municipal eme... | Relevant | 1 |
数据分布情况
数据是否倾斜
clean_questions.groupby("class_label").count() | Unnamed: 0 | text | choose_one | |
|---|---|---|---|
| class_label | |||
| 0 | 6187 | 6187 | 6187 |
| 1 | 4673 | 4673 | 4673 |
| 2 | 16 | 16 | 16 |
看起来还算均衡的
处理流程
- 分词
- 训练与测试集
- 检查与验证
from nltk.tokenize import RegexpTokenizertokenizer = RegexpTokenizer(r'\w+')clean_questions["tokens"] = clean_questions["text"].apply(tokenizer.tokenize)clean_questions.head()
| Unnamed: 0 | text | choose_one | class_label | tokens | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | just happened a terrible car crash | Relevant | 1 | [just, happened, a, terrible, car, crash] |
| 1 | 1 | our deeds are the reason of this earthquake m... | Relevant | 1 | [our, deeds, are, the, reason, of, this, earth... |
| 2 | 2 | heard about earthquake is different cities, s... | Relevant | 1 | [heard, about, earthquake, is, different, citi... |
| 3 | 3 | there is a forest fire at spot pond, geese are... | Relevant | 1 | [there, is, a, forest, fire, at, spot, pond, g... |
| 4 | 4 | forest fire near la ronge sask canada | Relevant | 1 | [forest, fire, near, la, ronge, sask, canada] |
语料库情况
from keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizerfrom keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequencesfrom keras.utils import to_categoricalall_words = [word for tokens in clean_questions["tokens"] for word in tokens]sentence_lengths = [len(tokens) for tokens in clean_questions["tokens"]]VOCAB = sorted(list(set(all_words)))print("%s words total, with a vocabulary size of %s" % (len(all_words), len(VOCAB)))print("Max sentence length is %s" % max(sentence_lengths)) 154724 words total, with a vocabulary size of 18101Max sentence length is 34
句子长度情况
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltfig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) plt.xlabel('Sentence length')plt.ylabel('Number of sentences')plt.hist(sentence_lengths)plt.show() 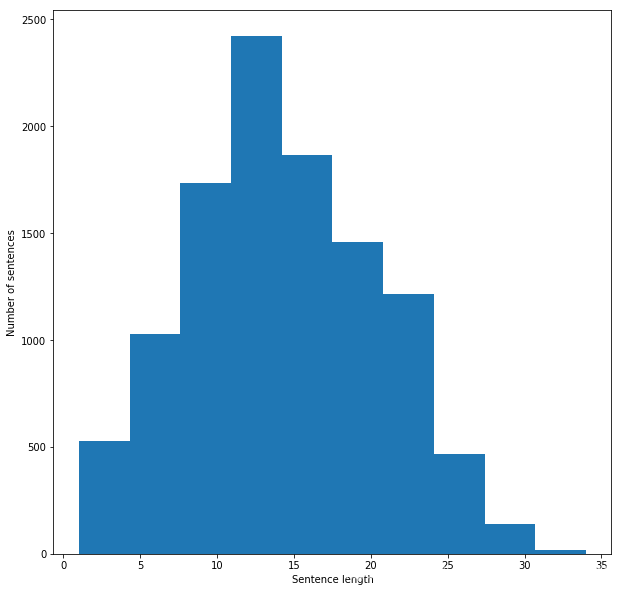
特征如何构建?
Bag of Words Counts
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer, TfidfVectorizerdef cv(data): count_vectorizer = CountVectorizer() emb = count_vectorizer.fit_transform(data) return emb, count_vectorizerlist_corpus = clean_questions["text"].tolist()list_labels = clean_questions["class_label"].tolist()X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(list_corpus, list_labels, test_size=0.2, random_state=40)X_train_counts, count_vectorizer = cv(X_train)X_test_counts = count_vectorizer.transform(X_test)
PCA展示Bag of Words
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA, TruncatedSVDimport matplotlibimport matplotlib.patches as mpatchesdef plot_LSA(test_data, test_labels, savepath="PCA_demo.csv", plot=True): lsa = TruncatedSVD(n_components=2) lsa.fit(test_data) lsa_scores = lsa.transform(test_data) color_mapper = { label:idx for idx,label in enumerate(set(test_labels))} color_column = [color_mapper[label] for label in test_labels] colors = ['orange','blue','blue'] if plot: plt.scatter(lsa_scores[:,0], lsa_scores[:,1], s=8, alpha=.8, c=test_labels, cmap=matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap(colors)) red_patch = mpatches.Patch(color='orange', label='Irrelevant') green_patch = mpatches.Patch(color='blue', label='Disaster') plt.legend(handles=[red_patch, green_patch], prop={ 'size': 30})fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 16)) plot_LSA(X_train_counts, y_train)plt.show() 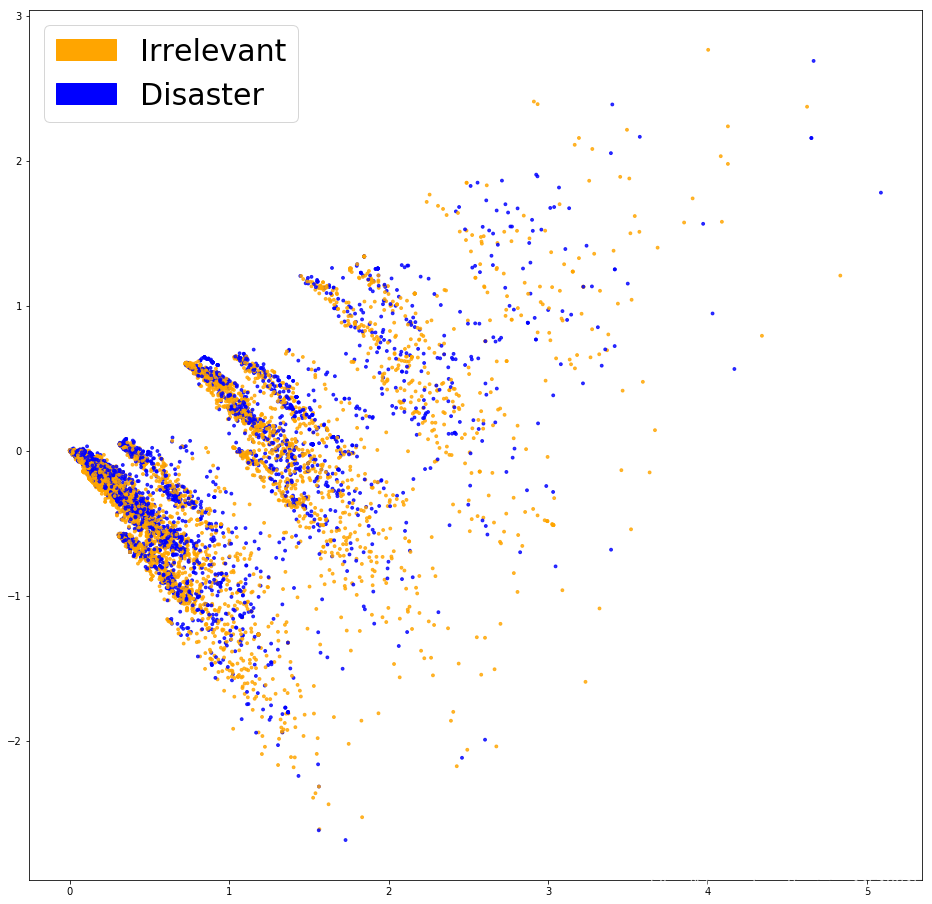
看起来并没有将这两类点区分开
逻辑回归看一下结果
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionclf = LogisticRegression(C=30.0, class_weight='balanced', solver='newton-cg', multi_class='multinomial', n_jobs=-1, random_state=40)clf.fit(X_train_counts, y_train)y_predicted_counts = clf.predict(X_test_counts)
评估
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, f1_score, precision_score, recall_score, classification_reportdef get_metrics(y_test, y_predicted): # true positives / (true positives+false positives) precision = precision_score(y_test, y_predicted, pos_label=None, average='weighted') # true positives / (true positives + false negatives) recall = recall_score(y_test, y_predicted, pos_label=None, average='weighted') # harmonic mean of precision and recall f1 = f1_score(y_test, y_predicted, pos_label=None, average='weighted') # true positives + true negatives/ total accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_predicted) return accuracy, precision, recall, f1accuracy, precision, recall, f1 = get_metrics(y_test, y_predicted_counts)print("accuracy = %.3f, precision = %.3f, recall = %.3f, f1 = %.3f" % (accuracy, precision, recall, f1)) accuracy = 0.754, precision = 0.752, recall = 0.754, f1 = 0.753
混淆矩阵检查
import numpy as npimport itertoolsfrom sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrixdef plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes, normalize=False, title='Confusion matrix', cmap=plt.cm.winter): if normalize: cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis] plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap) plt.title(title, fontsize=30) plt.colorbar() tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes)) plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, fontsize=20) plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes, fontsize=20) fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd' thresh = cm.max() / 2. for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])): plt.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt), horizontalalignment="center", color="white" if cm[i, j] < thresh else "black", fontsize=40) plt.tight_layout() plt.ylabel('True label', fontsize=30) plt.xlabel('Predicted label', fontsize=30) return plt cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_predicted_counts)fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))plot = plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes=['Irrelevant','Disaster','Unsure'], normalize=False, title='Confusion matrix')plt.show()print(cm)
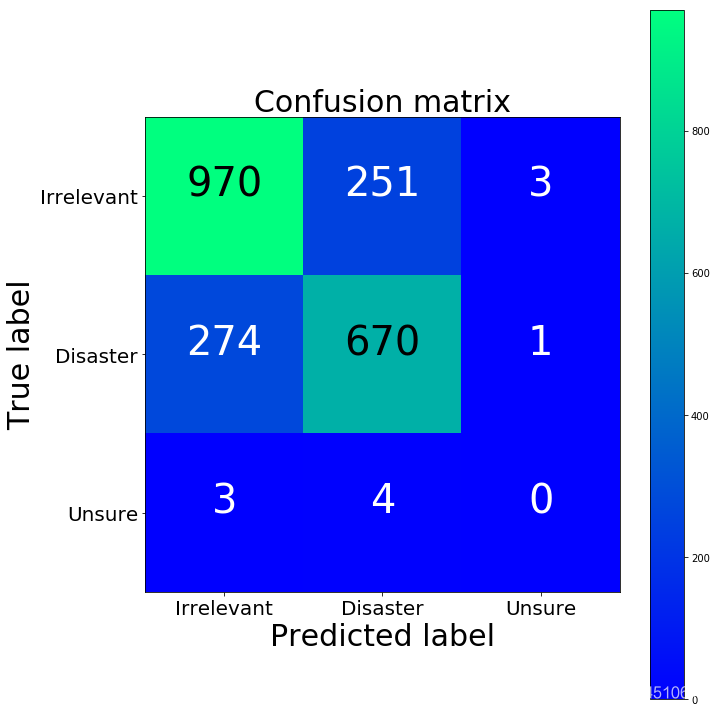
[[970 251 3] [274 670 1] [ 3 4 0]]
第三类咋没有一个呢。。。因为数据里面就没几个啊。。。
进一步检查模型的关注点
def get_most_important_features(vectorizer, model, n=5): index_to_word = { v:k for k,v in vectorizer.vocabulary_.items()} # loop for each class classes ={ } for class_index in range(model.coef_.shape[0]): word_importances = [(el, index_to_word[i]) for i,el in enumerate(model.coef_[class_index])] sorted_coeff = sorted(word_importances, key = lambda x : x[0], reverse=True) tops = sorted(sorted_coeff[:n], key = lambda x : x[0]) bottom = sorted_coeff[-n:] classes[class_index] = { 'tops':tops, 'bottom':bottom } return classesimportance = get_most_important_features(count_vectorizer, clf, 10) def plot_important_words(top_scores, top_words, bottom_scores, bottom_words, name): y_pos = np.arange(len(top_words)) top_pairs = [(a,b) for a,b in zip(top_words, top_scores)] top_pairs = sorted(top_pairs, key=lambda x: x[1]) bottom_pairs = [(a,b) for a,b in zip(bottom_words, bottom_scores)] bottom_pairs = sorted(bottom_pairs, key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True) top_words = [a[0] for a in top_pairs] top_scores = [a[1] for a in top_pairs] bottom_words = [a[0] for a in bottom_pairs] bottom_scores = [a[1] for a in bottom_pairs] fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10)) plt.subplot(121) plt.barh(y_pos,bottom_scores, align='center', alpha=0.5) plt.title('Irrelevant', fontsize=20) plt.yticks(y_pos, bottom_words, fontsize=14) plt.suptitle('Key words', fontsize=16) plt.xlabel('Importance', fontsize=20) plt.subplot(122) plt.barh(y_pos,top_scores, align='center', alpha=0.5) plt.title('Disaster', fontsize=20) plt.yticks(y_pos, top_words, fontsize=14) plt.suptitle(name, fontsize=16) plt.xlabel('Importance', fontsize=20) plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.8) plt.show()top_scores = [a[0] for a in importance[1]['tops']]top_words = [a[1] for a in importance[1]['tops']]bottom_scores = [a[0] for a in importance[1]['bottom']]bottom_words = [a[1] for a in importance[1]['bottom']]plot_important_words(top_scores, top_words, bottom_scores, bottom_words, "Most important words for relevance") 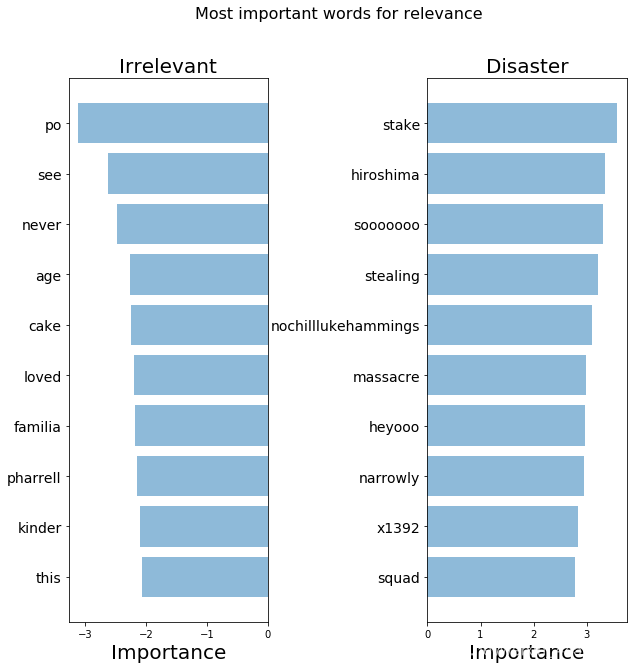
我们的模型找到了一些模式,但是看起来还不够好
TFIDF Bag of Words
这样我们就不均等对待每一个词了
def tfidf(data): tfidf_vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer() train = tfidf_vectorizer.fit_transform(data) return train, tfidf_vectorizerX_train_tfidf, tfidf_vectorizer = tfidf(X_train)X_test_tfidf = tfidf_vectorizer.transform(X_test)
F:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\sklearn\feature_extraction\text.py:1089: FutureWarning: Conversion of the second argument of issubdtype from `float` to `np.floating` is deprecated. In future, it will be treated as `np.float64 == np.dtype(float).type`. if hasattr(X, 'dtype') and np.issubdtype(X.dtype, np.float):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(16, 16)) plot_LSA(X_train_tfidf, y_train)plt.show()

看起来好那么一丁丁丁丁点
clf_tfidf = LogisticRegression(C=30.0, class_weight='balanced', solver='newton-cg', multi_class='multinomial', n_jobs=-1, random_state=40)clf_tfidf.fit(X_train_tfidf, y_train)y_predicted_tfidf = clf_tfidf.predict(X_test_tfidf)
accuracy_tfidf, precision_tfidf, recall_tfidf, f1_tfidf = get_metrics(y_test, y_predicted_tfidf)print("accuracy = %.3f, precision = %.3f, recall = %.3f, f1 = %.3f" % (accuracy_tfidf, precision_tfidf, recall_tfidf, f1_tfidf)) accuracy = 0.762, precision = 0.760, recall = 0.762, f1 = 0.761
cm2 = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_predicted_tfidf)fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))plot = plot_confusion_matrix(cm2, classes=['Irrelevant','Disaster','Unsure'], normalize=False, title='Confusion matrix')plt.show()print("TFIDF confusion matrix")print(cm2)print("BoW confusion matrix")print(cm) 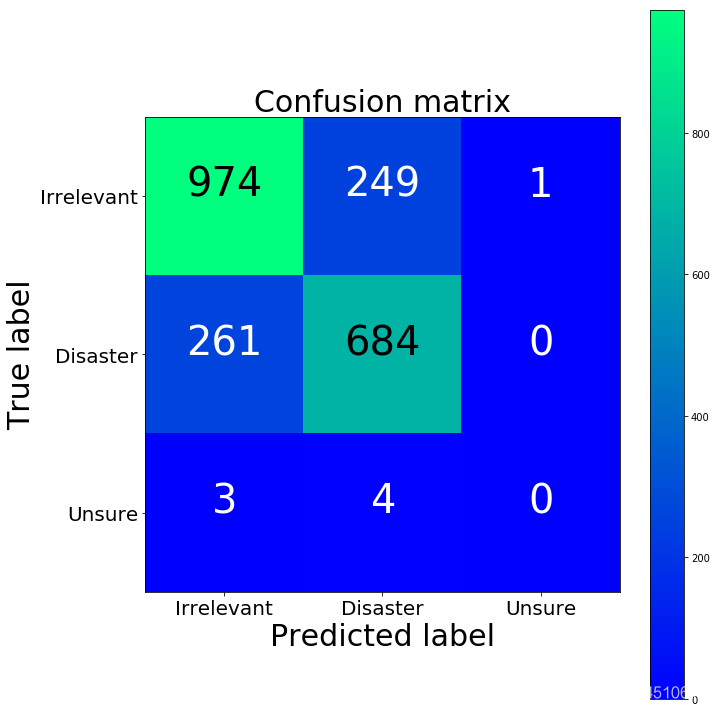
TFIDF confusion matrix[[974 249 1] [261 684 0] [ 3 4 0]]BoW confusion matrix[[970 251 3] [274 670 1] [ 3 4 0]]
词语的解释
importance_tfidf = get_most_important_features(tfidf_vectorizer, clf_tfidf, 10)
top_scores = [a[0] for a in importance_tfidf[1]['tops']]top_words = [a[1] for a in importance_tfidf[1]['tops']]bottom_scores = [a[0] for a in importance_tfidf[1]['bottom']]bottom_words = [a[1] for a in importance_tfidf[1]['bottom']]plot_important_words(top_scores, top_words, bottom_scores, bottom_words, "Most important words for relevance")
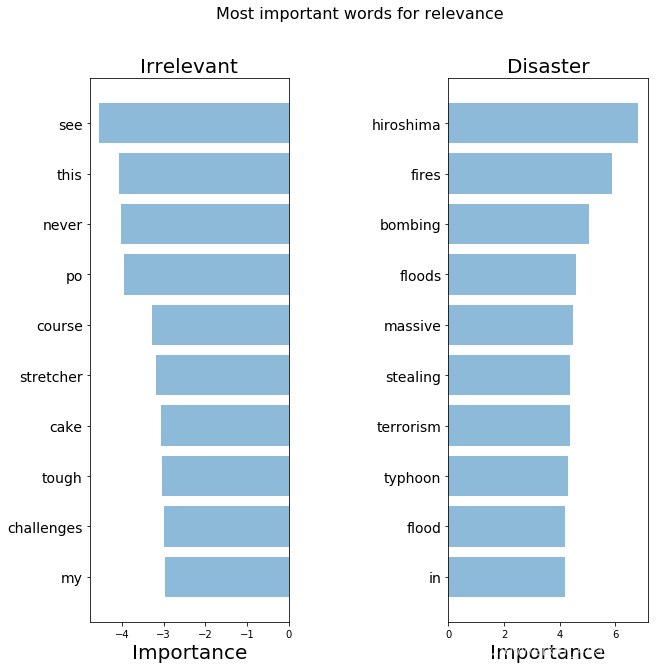
这些词看起来比之前强一些了
转载地址:https://maoli.blog.csdn.net/article/details/89455723 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
网站不错 人气很旺了 加油
[***.192.178.218]2024年04月23日 22时35分40秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
2021年不可错过的17种JS优化技巧(一)
2021-07-03
在 Vue 中用 Axios 异步请求API
2021-07-03
MySQL进阶查询(SELECT 语句高级用法)
2021-07-03
Mysql 之主从复制
2021-07-03
【NLP学习笔记】中文分词(Word Segmentation,WS)
2021-07-03
对于时间复杂度的通俗理解
2021-07-03
如何输入多组数据并输出每组数据的和?
2021-07-03
行阶梯型矩阵
2021-07-03
MATLAB指定路径保存图片方法
2021-07-03
JAVA学习笔记6 - 数组
2021-07-03
【学习笔记】Android Activity
2021-07-03
location区段
2021-07-03
nginx访问控制、基于用户认证、https配置
2021-07-03
linux内存的寻址方式
2021-07-03
how2heap-double free
2021-07-03
how2heap-fastbin_dup_consolidate
2021-07-03
tf keras SimpleRNN源码解析
2021-07-03
MyBatisPlus简单入门(SpringBoot)
2021-07-03
攻防世界web进阶区web2详解
2021-07-03