
本文共 4787 字,大约阅读时间需要 15 分钟。
github地址
可用于腾讯云SCF以及云开发环境 错误处理尚未完善 错误参考mysql错误 引入依赖包 npm install dmhsq-mysql-db 效果如下 简化了mysql的使用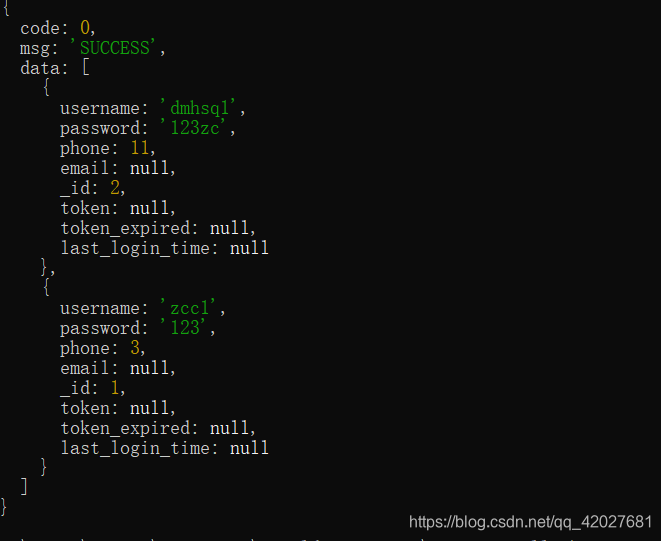
未经本人允许,禁止转载
nodejs环境快速操作mysql数据库
安装
普通版本 npm install dmhsq-mysql-db
数据连接池版本 npm install dmhsq-mysql-pool
使用示例
快速操作mysql 错误处理尚未完善 部分错误参考mysql错误
返回的均为Promise对象
所有操作结束末尾必须携带get()
比如 collection.sort({}).get() collection.del({}).get() collection.add({}).get()
所有操作除了get()必须末尾调用 都可以不分先后调用
比如 collection.sort({}).where().get()可以写出 collection.where().sort({}).get()
引入资源
const database = require("dmhsq-mysql-db") 连接数据库
let db = new database({ host: 'xxx', port: 'xxx', user: 'xxxx', password: 'xxxx', database: "xxxx"}) 引用表
let collection = db.table("user") 条件匹配
collection.where(params)
params 对象类型 格式为{username:“zc”,old:18} 其中username,old是你要查询的字段值
//如果需要获取数据 就要调用collection.where({username:"zcc"}).get()collection.where({ username:"zcc"}) 模糊匹配
collection.like(array)
array 数组类型 格式为[[“数据库键名1”,“值”,like],[“数据库键名2”,“值”,like]]
like 值可取 “top”:以字段开头的 “end”:是以字段结尾的 “in”:包含字段 输入其他非法值均以in处理
//如果需要获取数据 就要调用//collection.like([// ["username", "z", "top"],// ["old", "8", "end"],// ["address", "村", "in"]//]).get()collection.like([ ["username", "z", "top"], ["old", "8", "end"], ["address", "村", "in"]])
查询数据返回格式
模糊查询 条件查询 只要是查询 都是这个格式
data为查询到的数据 为数组类型
{ code: 0, msg: 'SUCCESS', data: [ //这里的返回数据 是模拟数据 { username: 'dmhsq1', password: '123zc', phone: 11, email: null, _id: 2, token: null, token_expired: null, last_login_time: null }, { username: 'zcc1', password: '123', phone: 3, email: null, _id: 1, token: null, token_expired: null, last_login_time: null } ]} 查询全部/获取数据
collection.get()
collection.get().then(res => { console.log(res)}) 统计个数
collection.count().get()
可搭配下面的where(条件查询) like(模糊查询)
collection.count().get().then(res => { console.log(res)}) 返回格式
{ code: 0, msg: 'SUCCESS', data: { count: 2 }, count: '查询到2个数据'} 条件查询
条件匹配+获取数据
collection.where(params).get()
params:对象类型 格式为 {数据库键1:“值”,数据库键2:“值”}
collection.where({ username: "dmhsq"}).get().then(res => { console.log(res)}) 模糊查询
模糊匹配+获取数据
collection.like(array).get()
array 数组类型 格式为[[“数据库键名1”,“值”,like],[“数据库键名2”,“值”,like]]
like 值可取 “top”:以字段开头的 “end”:是以字段结尾的 “in”:包含字段 输入其他非法值均以in处理
collection.like([ ["username", "z", "top"], ["old", "8", "end"], ["address", "村", "in"]]).get()
返回格式
{ code: 0, msg: 'SUCCESS', data: [ //这里的返回数据 是模拟数据 { username: 'dmhsq1', password: '123zc', phone: 11, email: null, _id: 2, token: null, token_expired: null, last_login_time: null }, { username: 'zcc1', password: '123', phone: 3, email: null, _id: 1, token: null, token_expired: null, last_login_time: null } ]} 插入数据
collection.add(params,isIgnore)
params:对象类型 格式为 {数据库键1:“值”,数据库键2:“值”}
isIgnore 可选 默认false 当为true时 使用 INSERT IGNORE INTO
collection.add({ username: "dmhsq", password: "dmhsq", _id: 123176312}).get().then(res => { console.log(res)}) 返回格式
{ code: 0, msg: 'SUCCESS', data: { add: 1 //数据增加个数 }, add: '增加1个数据'} 更新数据
collection.updata(params)
params:对象类型 格式为 {数据库键1:“值”,数据库键2:“值”}
可使用 where like
collection.updata({ password: "zccc", old:18}).where({ username: "dmhsq"}).get().then(res=>{ console.log(res)}) 删除数据
collection.del() 删除操作
可使用 where like
collection.del().where({ username: "dmhsq"}).get().then(res => { console.log(res)}) 返回格式
{ code: 0, msg: 'SUCCESS', data: { del: 1 }, del: '删除1个数据'} 返回指定字段(不添加会返回全部)
collection.field(array)
array:数组类型 格式为[“数据库键名1”,“数据库键名2”]
//获取全部collection.field(["username"]).get()//模糊匹配collection.field(["username"]).like({ username:"z"},"top").get().then(res=>{ console.log(res)})//条件匹配collection.field(["username"]).where({ username:"zcc"}).get().then(res=>{ console.log(res)}) 返回格式
{ code: 0, msg: 'SUCCESS', data: [{ username: 'zcc1', _id: 1 }, { username: 'dmhsq1', _id: 2 }]} 排序
collection.sort(params)
params:对象类型 格式为 {数据库键名1:“DESC”,数据库键名2:“ASC”}
DESC为降序 ASC降序
单个字段
collection.sort({_id:“DESC”})多个字段
collection.sort({_id:“DESC”,phone:“DESC”})collection.sort({ _id:"DESC",phone:"DESC"}).like({ username:"1"},"in").get().then(res=>{ console.log(res)})//或者collection.like({ username:"1"},"in").sort({ _id:"DESC",phone:"DESC"}).get().then(res=>{ console.log(res)}) 排序后返回的数据格式和查询数据结果格式一样
自定义查询语句
如果以上方法无法满足您的需求 您可以自定义查询语句
collection.sqlQuery(sql,type)
sql为自定义查询语句
type可不填 不填自动识别操作类型
type不影响查询 只是格式化返回的数据格式
type可选值为 updata(更新) del(删除) count(计数) add(插入)
无需后缀添加get()
//如果是查询数据库数据collection.sqlQuery("SELECT * FROM user").then(res=>{ console.log(res)})//如果是删除数据collection.sqlQuery("DELETE FROM user WHERE username = 'zcc2'").then(res=>{ console.log(res)}) 转载地址:https://dmhsq.blog.csdn.net/article/details/115038010 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
