本文共 13663 字,大约阅读时间需要 45 分钟。
根据web.xml配置我们知道.DispatcherServlet这个类是Spring MVC的关键类。Spring的方法命名很有趣,在Spring进行DI注入的时候,也就是当Application调用getBean方法的时候。getBean方法调用的是doGetBean.而Spring MVC在处理request对象的时候调用的是doService方法。
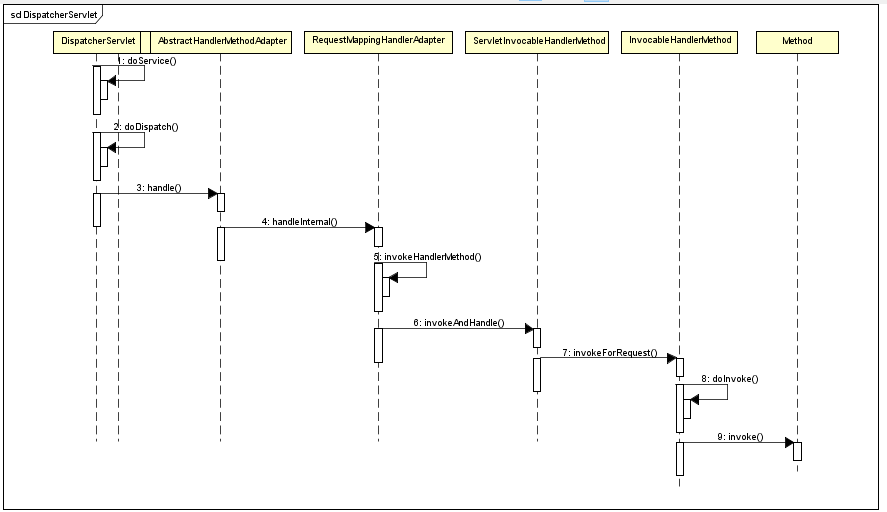
调用时序图:
通过上面这张时序调用图我们可以看到Dispatcher最终用使用反射调用Method中的invoke方法。而这个方法就是Controller当中的定义的@RequestMapping方法。可以看看之前我的Blog – 。整个从用户request,到服务器response都可以串联起来。下面我们来具体看一看是怎么调用的。
1、doService – Spring MVC处理请求入口
我们来看看处于DispatcherServlet的doService方法。
/** * Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch} * for the actual dispatching. */@Overrideprotected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : ""; logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed + " processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]"); } // Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include, // to be able to restore the original attributes after the include. Map attributesSnapshot = null; if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { attributesSnapshot = new HashMap (); Enumeration attrNames = request.getAttributeNames(); while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) { String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement(); if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith("org.springframework.web.servlet")) { attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName)); } } } // 1、提供框架对象处理程序和视图对象。(也就是Spring MVC中特殊的几个bean) request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext()); // 2、spring mvc支持i18n request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver); // 3、spring mvc支持主题 request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver); request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource()); // 4、springn mvc支持POST/Redirect/GET模式问题 FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response); if (inputFlashMap != null) { request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap)); } request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap()); request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager); try { // 5、spring mvc分发前端request doDispatch(request, response); } finally { if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include. if (attributesSnapshot != null) { restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot); } } }} 这个方法主要的功能实现都在是doDispatch方法中。我们来看一看这个方法。
2、doDispatch – 进行request分发处理的整个流程
下面我们来看看同样处于DispatcherServlet中的doDispatch方法。
/** * Process the actual dispatching to the handler. *The handler will be obtained by applying the servlet's HandlerMappings in order. * The HandlerAdapter will be obtained by querying the servlet's installed HandlerAdapters * to find the first that supports the handler class. *
All HTTP methods are handled by this method. It's up to HandlerAdapters or handlers * themselves to decide which methods are acceptable. * @param request current HTTP request * @param response current HTTP response * @throws Exception in case of any kind of processing failure */protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { // 步骤1、检查是否是请求是否是multipart(如文件上传),如果是将通过MultipartResolver解析 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // 步骤2、请求到处理器(页面控制器)的映射,通过HandlerMapping进行映射 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // 步骤3、处理器适配,即将我们的处理器包装成相应的适配器(从而支持多种类型的处理器) HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // 步骤4、如果处理程序支持,处理header中包含last-modified String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // 步骤5、真正调用适配器执行处理器(这里是调用Controller的入口) mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } // 步骤6、由ViewResolver解析View(viewResolver.resolveViewName(viewName, locale)) applyDefaultViewName(request, mv); // 步骤7、执行HandlerInterceptor链,并执行post处理 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } // 步骤8、渲染视图(包含对异常的处理) processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Error err) { triggerAfterCompletionWithError(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, err); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } }}
3、handle – 调用Controller的入口
这个方法位于org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter#handle()中。
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);} 其实由上面传过来的handler就是HandlerMethod.就样就合Controller关联了起来。看到这个方法我们下一步就是跟进handleInternal这个方法中去看看。
4、handleInternal – 判断Controller是否使用了@SessionAttributes
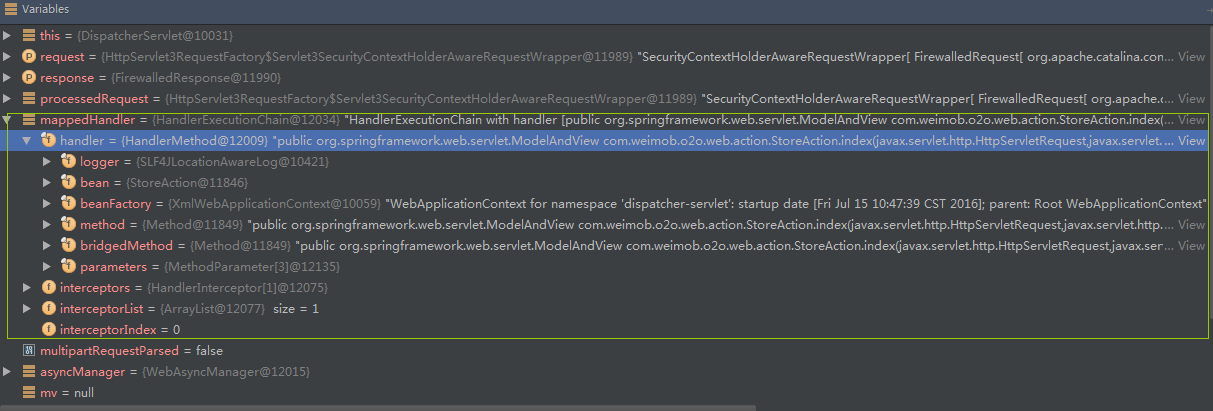
这个方法位于org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter#handleInternal()中。RequestMappingHandlerAdapter这个类非常重要,我们可以先来看一下它的属性。
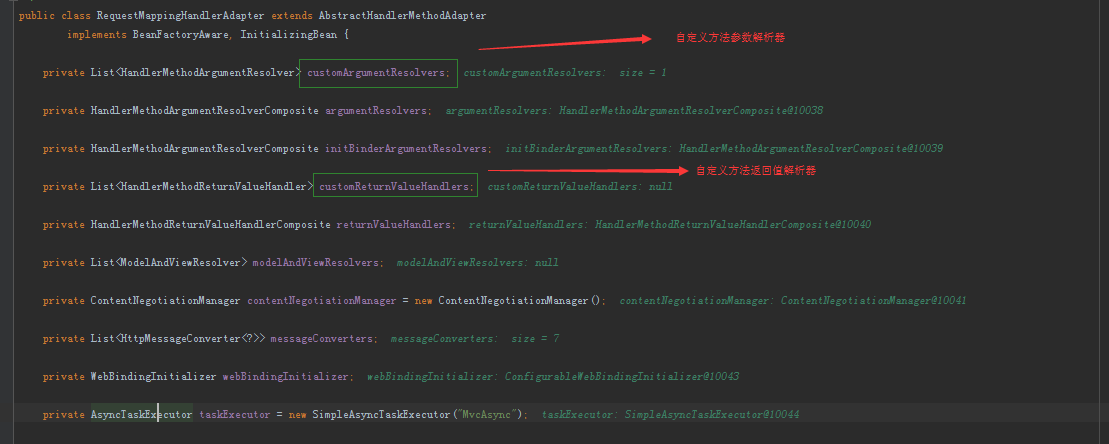 Spring MVC不是有支持的方法参数,以及方法返回参数。看到这个类信息,我们就是通过自定义方法参数与自定义方法返回参数来对Spring MVC进行扩展。后面我会用我们项目中的实例来讲解这个功能。这里主要是想给大家打开一个思路。扩展解决问题的方法。 下面我们看看这个方法的具体实现:
Spring MVC不是有支持的方法参数,以及方法返回参数。看到这个类信息,我们就是通过自定义方法参数与自定义方法返回参数来对Spring MVC进行扩展。后面我会用我们项目中的实例来讲解这个功能。这里主要是想给大家打开一个思路。扩展解决问题的方法。 下面我们看看这个方法的具体实现: @Overrideprotected final ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) { // Always prevent caching in case of session attribute management. checkAndPrepare(request, response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers, true); } else { // Uses configured default cacheSeconds setting. checkAndPrepare(request, response, true); } // Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required. if (this.synchronizeOnSession) { HttpSession session = request.getSession(false); if (session != null) { Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session); synchronized (mutex) { return invokeHandleMethod(request, response, handlerMethod); } } } // 1、invoke handlerMethod return invokeHandleMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);} 调用invoke handlerMethod就是调用Controller具体处理这个请求的方法,我们接着往下看。
5、invokeHandleMethod – 真正分发request处理(异步处理),并创建ModelAndView包装类
这个方法位于org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter#invokeHandleMethod()中。
/** * Invoke the {@link RequestMapping} handler method preparing a {@link ModelAndView} * if view resolution is required. */ private ModelAndView invokeHandleMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); ServletInvocableHandlerMethod requestMappingMethod = createRequestMappingMethod(handlerMethod, binderFactory); // ModelAndView包装类 ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request)); modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, requestMappingMethod); mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect); // DispatcherServlet,就是用于分发请求。而AsyncWebRequest就是异步处理页面请求 AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response); asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout); // 异步请求处理器 final WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor); asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors); asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors); if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) { Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult(); mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0]; asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult(); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Found concurrent result value [" + result + "]"); } requestMappingMethod = requestMappingMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result); } // requestMappingMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return null; } return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest); } 6、invokeAndHandle – 调用请求处理,并对ModelAndView包装类进行值添加
这个方法位于org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle()
/** * Invokes the method and handles the return value through a registered * {@link HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler}. * * @param webRequest the current request * @param mavContainer the ModelAndViewContainer for this request * @param providedArgs "given" arguments matched by type, not resolved */public final void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { // 看名字我们就知道这个方法是干什么的了,没错,继续进去。 Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs); setResponseStatus(webRequest); if (returnValue == null) { if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || hasResponseStatus() || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) { mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true); return; } } else if (StringUtils.hasText(this.responseReason)) { mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true); return; } mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false); try { this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue(returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest); } catch (Exception ex) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(getReturnValueHandlingErrorMessage("Error handling return value", returnValue), ex); } throw ex; }} 7、invokeForRequest – 利用反射调用Contoller处理Request的方法
public final Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { // 1、获取这个方法的请求参数 Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Invoking ["); sb.append(getBeanType().getSimpleName()).append("."); sb.append(getMethod().getName()).append("] method with arguments "); sb.append(Arrays.asList(args)); logger.trace(sb.toString()); } // 2、利用反射调用Contoller中的方法 Object returnValue = invoke(args); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Method [" + getMethod().getName() + "] returned [" + returnValue + "]"); } return returnValue;} 我们可以看看args的值。
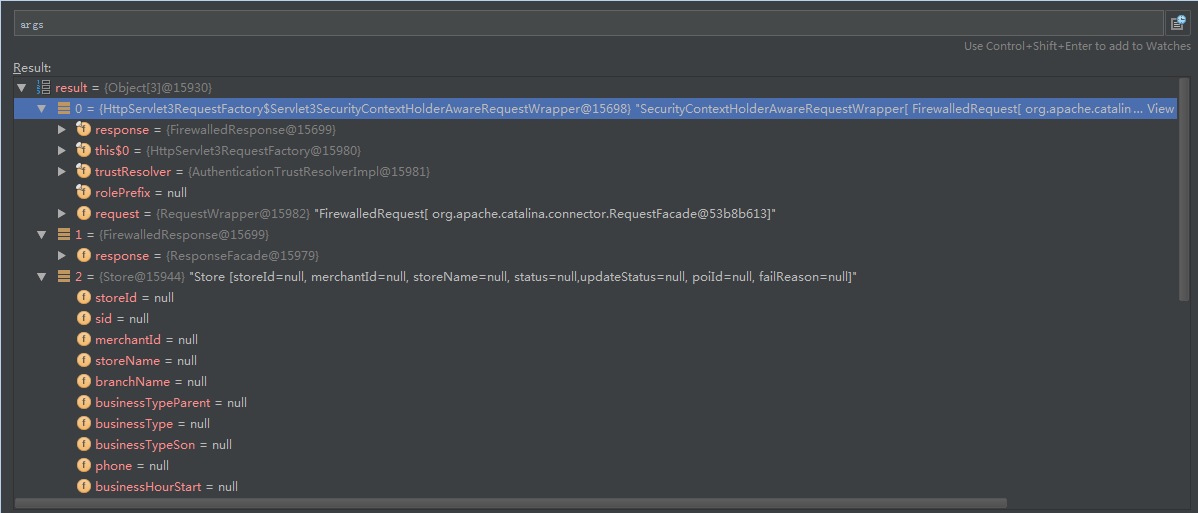 这些值就是Controller对应的请求参数。 那个invoke方法我们就没有必要分析了。以后进入的断点也是进入Controller的指定处理对应的URL的方法中。这样是不是@RequestMapping与Controller之间的关系,也就是页面请求到进入到Controller是不是理清了。后面就是怎么把页面渲染出来的了。这个问题会在以后的blog中分析的。
这些值就是Controller对应的请求参数。 那个invoke方法我们就没有必要分析了。以后进入的断点也是进入Controller的指定处理对应的URL的方法中。这样是不是@RequestMapping与Controller之间的关系,也就是页面请求到进入到Controller是不是理清了。后面就是怎么把页面渲染出来的了。这个问题会在以后的blog中分析的。 转载地址:https://carlzone.blog.csdn.net/article/details/51920055 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者