
本文共 5948 字,大约阅读时间需要 19 分钟。
要想了解决Spring MVC是怎么把@RequestMapping注解了的方法以及类解析的,首先我们需要关注AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#afterPropertiesSet这个方法,而这个方法是Spring的init方法,是Spring在进行初始化bean之前在DI注入之后调用到的方法。所以当Spring容器初始化之后,@RequestMapping就会被解析成Spring容器的bean管理。通过这个方法的说明也能验证之前所说的。我们首先来关注一下@RequestMapping的时序图:
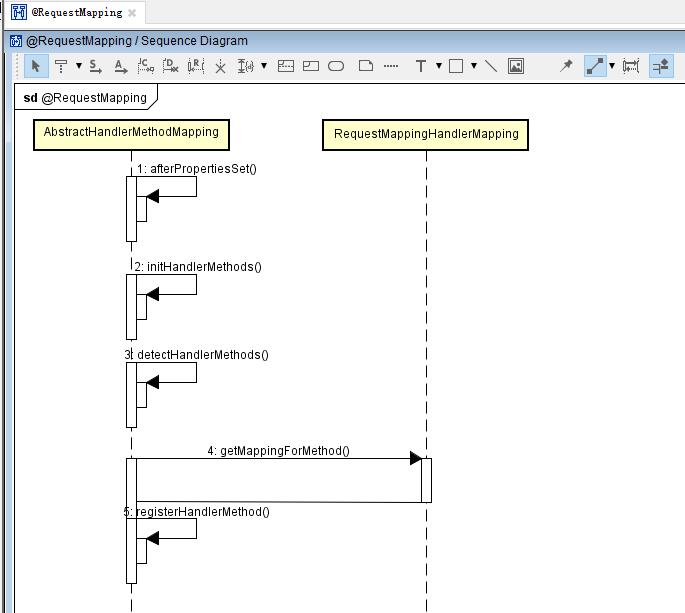
下面就入口方法。
/** * Detects handler methods at initialization. */public void afterPropertiesSet() { initHandlerMethods();} 1、初始化处理client页面request的方法
下面我们就要重点关注AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#initHandlerMethods这个方法了。
/** * Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods. * @see #isHandler(Class) * @see #getMappingForMethod(Method, Class) * @see #handlerMethodsInitialized(Map) */protected void initHandlerMethods() { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext()); } // 读取Spring容器中的所有beanNames String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); // 遍历这些bean,检测出处理方法 for (String beanName : beanNames) { // 判断这个bean是不是处理类(根据这个类是否使用了@Controller或@RequestMapping) if (isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){ detectHandlerMethods(beanName); } } // 处理方法后期处理,Spring空实现,方便以后扩展 handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());} 那么我们的关注点就需要放在detectHandlerMethods这个方法上了。
2、detectHandlerMethods
下面我们再来看一下AbstractHandlerMethodMapping#detectHandlerMethods这个方法。
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) { // 从Spring容器中获取这个类 Class handlerType = (handler instanceof String ? getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass()); // Avoid repeated calls to getMappingForMethod which would rebuild RequestMatchingInfo instances final Map mappings = new IdentityHashMap (); final Class userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); // 从处理类(@Controller)中获取处理方法(@RequestMapping) Set methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() { public boolean matches(Method method) { T mapping = getMappingForMethod(method, userType); if (mapping != null) { mappings.put(method, mapping); return true; } else { return false; } } }); // 注册方法, for (Method method : methods) { registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mappings.get(method)); }} 3、getMappingForMethod
Spring MVC通过RequestMappingHandlerMapping#getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class
/** * Uses method and type-level @{ @link RequestMapping} annotations to create * the RequestMappingInfo. * @return the created RequestMappingInfo, or { @code null} if the method * does not have a { @code @RequestMapping} annotation. * @see #getCustomMethodCondition(Method) * @see #getCustomTypeCondition(Class) */@Overrideprotected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class handlerType) { RequestMappingInfo info = null; // 这个方法是否使用@RequestMapping信息 RequestMapping methodAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class); if (methodAnnotation != null) { // 空实现,方便以后扩展 RequestCondition methodCondition = getCustomMethodCondition(method); // 创建RequestMappingInfo比较简单,如果感兴趣可以自己去看看 info = createRequestMappingInfo(methodAnnotation, methodCondition); // 查询这个Controller上面使用@RequestMapping信息 RequestMapping typeAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, RequestMapping.class); if (typeAnnotation != null) { // 空实现,方便以后扩展 RequestCondition typeCondition = getCustomTypeCondition(handlerType); // 把Class上面的@RequestMapping信息与方法上的@RequestMapping信息合并起来 info = createRequestMappingInfo(typeAnnotation, typeCondition).combine(info); } } return info;} 返回info主要是包含@RequestMapping的标签信息,我们可以看看info中的信息:
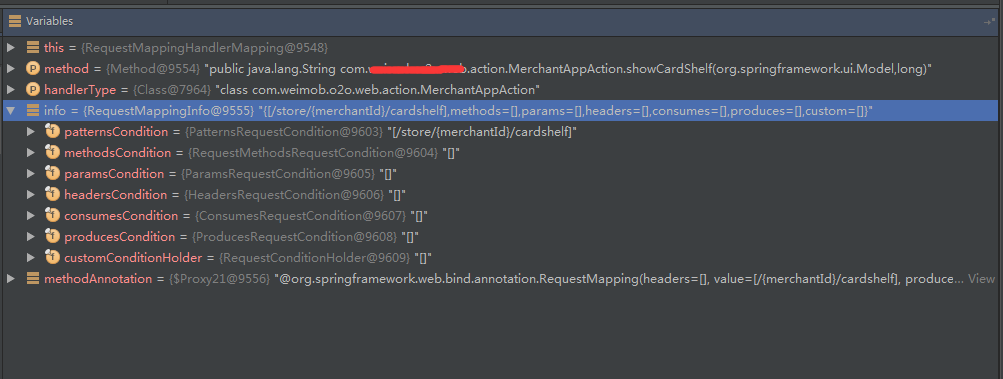
4、registerHandlerMethod
然后我们就关注一下。第二步中的detectHandlerMethods方法中的registerHandlerMethod方法。
/** * Register a handler method and its unique mapping. * @param handler the bean name of the handler or the handler instance * @param method the method to register * @param mapping the mapping conditions associated with the handler method * @throws IllegalStateException if another method was already registered * under the same mapping */protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = this.handlerMethods.get(mapping); if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) { throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map '" + newHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method \n" + newHandlerMethod + "\nto " + mapping + ": There is already '" + oldHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method\n" + oldHandlerMethod + " mapped."); } // 防止定义相同的处理映射 this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + newHandlerMethod); } Set patterns = getMappingPathPatterns(mapping); // 存在URL与RequestMappingInfo的映射 for (String pattern : patterns) { if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) { this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping); } }} 现在我们来看看这个解析之后这个类之中属性。
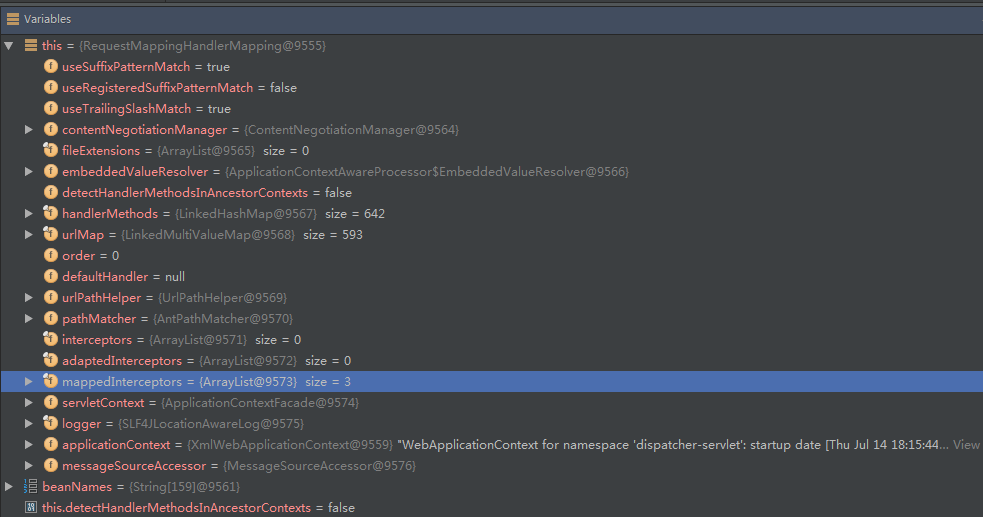 我们主要把关注点停留到urlMap与handlerMethods上。 1、urlMap
我们主要把关注点停留到urlMap与handlerMethods上。 1、urlMap 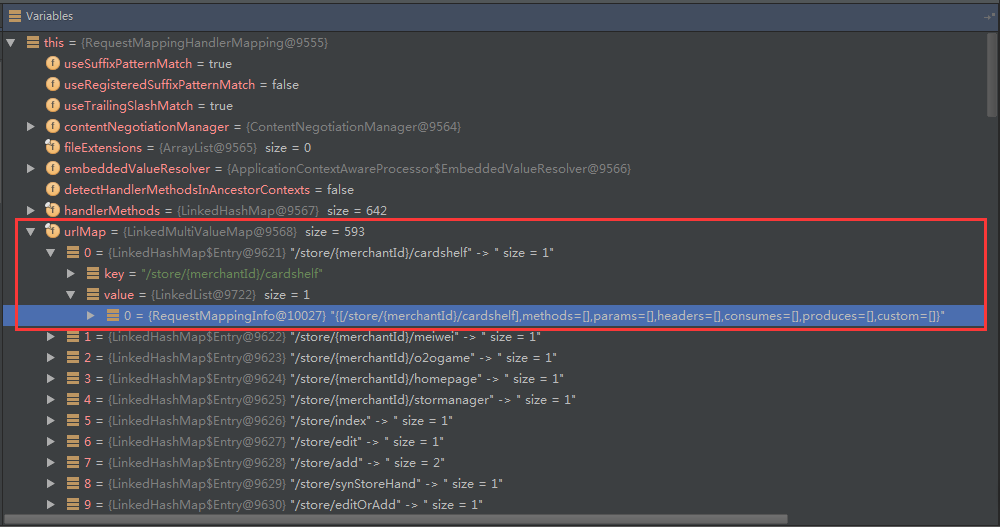 我们可以看到urlMap属性中保存的是请求路径与RequestMappingInfo的映射信息。 2、handerMethods
我们可以看到urlMap属性中保存的是请求路径与RequestMappingInfo的映射信息。 2、handerMethods 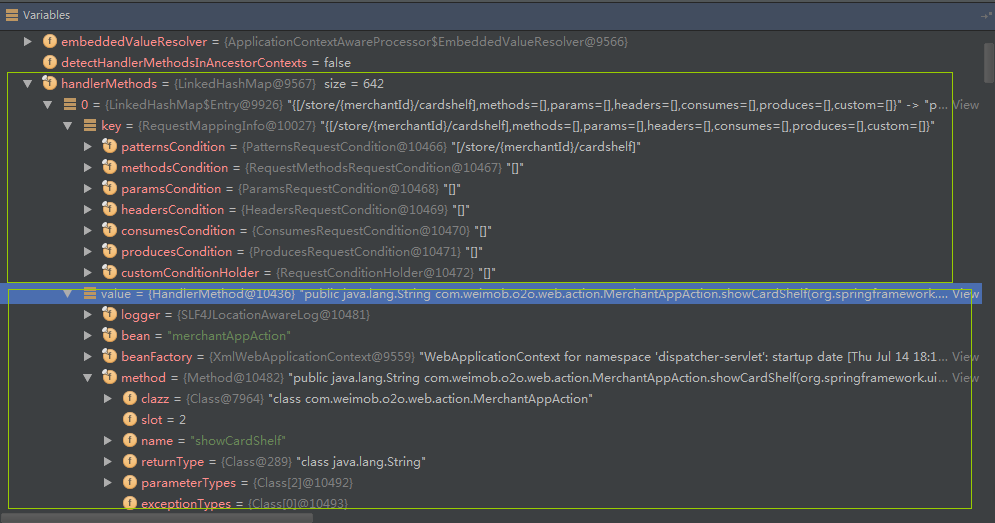 我们可以看到handerMethods属性中保存的是RequestMappingInfo与HanderMethod的映射。HanderMethod主要保存这个类与处理请求具体的方法。
我们可以看到handerMethods属性中保存的是RequestMappingInfo与HanderMethod的映射。HanderMethod主要保存这个类与处理请求具体的方法。 当页面有url请求过来.首先通过urlMap查询RequestMappingInfo的信息,然后再通过handerMethods查询到HanderMethod的信息。这样url请求是不是与Controller中的方法结合了起来。具体是怎么调用的,可以看看我写的Blog –
转载地址:https://carlzone.blog.csdn.net/article/details/51912375 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
