
本文共 4869 字,大约阅读时间需要 16 分钟。
(1)简介
Deep Learning最简单的一种方法是利用人工神经网络的特点,人工神经网络(ANN)本身就是具有层次结构的系统,如果给定一个神经网络,我们假设其输出与输入是相同的,然后训练调整其参数,得到每一层中的权重。自然地,我们就得到了输入I的几种不同表示(每一层代表一种表示),这些表示就是特征。自动编码器就是一种尽可能复现输入信号的神经网络。为了实现这种复现,自动编码器就必须捕捉可以代表输入数据的最重要的因素,就像PCA那样,找到可以代表原信息的主要成分。
具体过程简单的说明如下:
1)给定无标签数据,用非监督学习学习特征:

在我们之前的神经网络中,如第一个图,我们输入的样本是有标签的,即(input, target),这样我们根据当前输出和target(label)之间的差去改变前面各层的参数,直到收敛。但现在我们只有无标签数据,也就是右边的图。那么这个误差怎么得到呢?

如上图,我们将input输入一个encoder编码器,就会得到一个code,这个code也就是输入的一个表示,那么我们怎么知道这个code表示的就是input呢?我们加一个decoder解码器,这时候decoder就会输出一个信息,那么如果输出的这个信息和一开始的输入信号input是很像的(理想情况下就是一样的),那很明显,我们就有理由相信这个code是靠谱的。所以,我们就通过调整encoder和decoder的参数,使得重构误差最小,这时候我们就得到了输入input信号的第一个表示了,也就是编码code了。因为是无标签数据,所以误差的来源就是直接重构后与原输入相比得到。
(2)代码
import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.utils.data as Dataimport torchvisionimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3Dfrom matplotlib import cmimport numpy as np# torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible# Hyper ParametersEPOCH = 10BATCH_SIZE = 64LR = 0.005 # learning rateDOWNLOAD_MNIST = FalseN_TEST_IMG = 5# Mnist digits datasettrain_data = torchvision.datasets.MNIST( root='./mnist/', train=True, # this is training data transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(), # Converts a PIL.Image or numpy.ndarray to # torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W) and normalize in the range [0.0, 1.0] download=DOWNLOAD_MNIST, # download it if you don't have it)# plot one exampleprint(train_data.train_data.size()) # (60000, 28, 28)print(train_data.train_labels.size()) # (60000)plt.imshow(train_data.train_data[2].numpy(), cmap='gray')plt.title('%i' % train_data.train_labels[2])plt.show()# Data Loader for easy mini-batch return in training, the image batch shape will be (50, 1, 28, 28)train_loader = Data.DataLoader(dataset=train_data, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True)class AutoEncoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(AutoEncoder, self).__init__() self.encoder = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(28*28, 128), nn.Tanh(), nn.Linear(128, 64), nn.Tanh(), nn.Linear(64, 12), nn.Tanh(), nn.Linear(12, 3), # compress to 3 features which can be visualized in plt ) self.decoder = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(3, 12), nn.Tanh(), nn.Linear(12, 64), nn.Tanh(), nn.Linear(64, 128), nn.Tanh(), nn.Linear(128, 28*28), nn.Sigmoid(), # compress to a range (0, 1) ) def forward(self, x): encoded = self.encoder(x) decoded = self.decoder(encoded) return encoded, decodedautoencoder = AutoEncoder()optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(autoencoder.parameters(), lr=LR)loss_func = nn.MSELoss()# initialize figuref, a = plt.subplots(2, N_TEST_IMG, figsize=(5, 2))plt.ion() # continuously plot# original data (first row) for viewingview_data = train_data.train_data[:N_TEST_IMG].view(-1, 28*28).type(torch.FloatTensor)/255.for i in range(N_TEST_IMG): a[0][i].imshow(np.reshape(view_data.data.numpy()[i], (28, 28)), cmap='gray'); a[0][i].set_xticks(()); a[0][i].set_yticks(())for epoch in range(EPOCH): for step, (x, b_label) in enumerate(train_loader): b_x = x.view(-1, 28*28) # batch x, shape (batch, 28*28) b_y = x.view(-1, 28*28) # batch y, shape (batch, 28*28) encoded, decoded = autoencoder(b_x) loss = loss_func(decoded, b_y) # mean square error optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for this training step loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients optimizer.step() # apply gradients if step % 100 == 0: print('Epoch: ', epoch, '| train loss: %.4f' % loss.data.numpy()) # plotting decoded image (second row) _, decoded_data = autoencoder(view_data) for i in range(N_TEST_IMG): a[1][i].clear() a[1][i].imshow(np.reshape(decoded_data.data.numpy()[i], (28, 28)), cmap='gray') a[1][i].set_xticks(()); a[1][i].set_yticks(()) plt.draw(); plt.pause(0.05)plt.ioff()plt.show()# visualize in 3D plotview_data = train_data.train_data[:200].view(-1, 28*28).type(torch.FloatTensor)/255.encoded_data, _ = autoencoder(view_data)fig = plt.figure(2); ax = Axes3D(fig)X, Y, Z = encoded_data.data[:, 0].numpy(), encoded_data.data[:, 1].numpy(), encoded_data.data[:, 2].numpy()values = train_data.train_labels[:200].numpy()for x, y, z, s in zip(X, Y, Z, values): c = cm.rainbow(int(255*s/9)); ax.text(x, y, z, s, backgroundcolor=c)ax.set_xlim(X.min(), X.max()); ax.set_ylim(Y.min(), Y.max()); ax.set_zlim(Z.min(), Z.max())plt.show()(3)结果
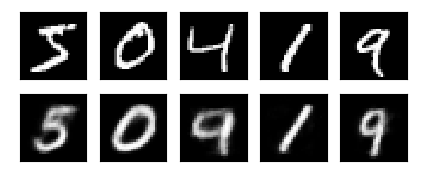

注:代码主要参考:
文章主要参考:
更多《计算机视觉与图形学》知识,可关注下方公众号:
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
