
Java笔记:单链表
编程题:
发布日期:2021-05-08 06:37:22
浏览次数:9
分类:原创文章
本文共 24933 字,大约阅读时间需要 83 分钟。
单链表
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的引用链接次序实现的。
链表的结构有很多,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
- 单向,双向
- 带头,不带头
- 循环,非循环
我们只需掌握两种结构:
(1)无头单向非循环链表。
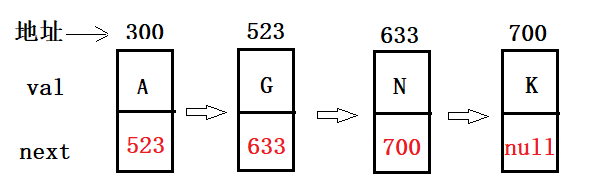
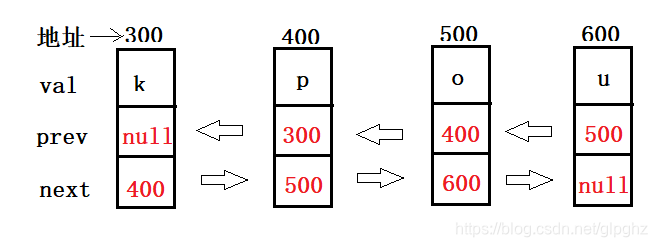
(2)无头双向链表:LinkedList的底层实现,双向链表都有一个prev和next, 链表最开始的部分都有一个fiest和last 指向第一个元素和最后一个元素。
链接:
注意:
- 不支持随机访问
- 任意位置插入删除时间复杂度为O(1)
题目列表
编程题:
[1]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode newHead=null; ListNode prev=null; ListNode cur = head; while(cur!=null){ ListNode curNext = cur.next; if(curNext==null){ newHead=cur; } cur.next=prev; prev=cur; cur=curNext; } return newHead; }}[2]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */class Solution { public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) { if(head==null){ return null; } if(head.val==val){ return head = head.next; } ListNode prev = search(head,val); if(prev==null){ return null; }else{ prev.next = prev.next.next; } return head; } public ListNode search(ListNode head,int val){ ListNode cur=head; while(cur.next!=null){ if(cur.next.val==val){ return cur; } cur=cur.next; } return null; }}[3]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { if(head==null){ return null; } ListNode prev = head; ListNode cur = head.next; while(cur!=null){ if(cur.val == val){ prev.next = cur.next; cur = cur.next; }else{ prev = cur; cur = cur.next; } } if(head.val ==val){ head = head.next; } return head; }}[4]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */class Solution { public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode low =head; while(fast!=null&&fast.next!=null){ fast= fast.next.next; low = low.next; } return low; }}[5]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */class Solution { public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) { if(k<=0){ return null; } ListNode fast = head; ListNode low = head; while(k-1>0){ if(fast==null){ return null; } fast = fast.next; k--; } while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){ fast = fast.next; low = low.next; } return low; }}[6]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */class Solution { public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) { if(head==null){ return null; } ListNode as=null; ListNode ae=null; ListNode bs=null; ListNode be=null; ListNode cur = head; while(cur!=null){ if(cur.val<x){ if(as==null){ as = cur; ae = cur; }else{ ae.next = cur; ae = ae.next; } }else{ if(bs == null){ bs = cur; be = cur; }else{ be.next = cur; be = be.next; } } cur = cur.next; } if(bs==null){ return as; } if(as==null){ return bs; } ae.next = bs; be.next = null; return as; }}[7]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */class Solution { public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) { if(head ==null){ return null; } ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1); ListNode tmp = newHead; ListNode cur = head; while(cur!=null){ if(cur.next!=null && cur.val == cur.next.val){ while(cur.next!=null && cur.val == cur.next.val){ cur =cur.next; } cur = cur.next; }else{ tmp.next = cur; tmp = tmp.next; cur = cur.next; } } tmp.next = null; return newHead.next; }}[8]
涉及到了寻找中间节点及反转链表。
import java.util.*;/*public class ListNode { int val; ListNode next = null; ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }}*/public class PalindromeList { public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) { // write code here if(A==null){ return true; } //寻找中间节点 ListNode fast = A; ListNode low = A; while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){ fast = fast.next.next; low = low.next; } //反转链表 ListNode prev = low; ListNode cur = low.next; while(cur!=null){ ListNode curNext = cur.next; cur.next = prev; prev = cur; cur = curNext; } //判断回文 //节点个数为奇数和偶数时的情况 prev!=A && A.next!=prev while(prev!=A && A.next!=prev){ if(prev.val!=A.val){ return false; } prev = prev.next; A = A.next; } return true; }}[9]
如果有环的话,fast和low一定会相交。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */public class Solution { public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) { if(head==null){ return false; } ListNode fast = head; ListNode low = head; while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){ fast = fast.next.next; low = low.next; if(fast==low){ return true; } } return false; }}[10]
通过fast.next.next和low.next第一次相遇之后,让low回到头节点,再通过low.next和fast.next,若再次相遇,则相遇点即为入环节点。
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { if(head==null){ return null; } ListNode fast = head; ListNode low = head; while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){ fast = fast.next.next; low = low.next; if(fast == low){ break; } } if(fast==null || fast.next==null){ return null; } low =head; while(fast!=low){ fast = fast.next; low = low.next; } return low; }}[11]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode() {} * ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } * ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } * } */class Solution { public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) { ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1); ListNode tmp = newHead; while(l1!=null && l2!=null){ if(l1.val<=l2.val){ tmp.next = l1; tmp = tmp.next; l1 = l1.next; }else{ tmp.next = l2; tmp = tmp.next; l2 = l2.next; } } if(l1!=null){ tmp.next = l1; } if(l2!=null){ tmp.next = l2; } return newHead.next; }}[12]
/** * Definition for singly-linked list. * public class ListNode { * int val; * ListNode next; * ListNode(int x) { * val = x; * next = null; * } * } */public class Solution { public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { ListNode l1 = headA; ListNode l2 = headB; int lenA=0; int lenB=0; while(l1!=null){ lenA++; l1 = l1.next; } while(l2!=null){ lenB++; l2 = l2.next; } int len = lenA-lenB; l1 = headA; l2 = headB; if(len<0){ l1=headB; l2=headA; len=-len; } while(len>0){ l1 = l1.next; len--; } while(l1!=null && l2!=null){ if(l1==l2){ return l1; } l1 = l1.next; l2 = l2.next; } return null; }}[13]
用hashMap来解决比较容易一些。
详细内容可参考博客:
/*// Definition for a Node.class Node { int val; Node next; Node random; public Node(int val) { this.val = val; this.next = null; this.random = null; }}*/class Solution { public Node copyRandomList(Node head) { HashMap<Node,Node> map = new HashMap<>(); Node cur = head; while(cur!=null){ Node node = new Node(cur.val); map.put(cur,node); cur = cur.next; } cur = head; while(cur!=null){ map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next); map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random); cur = cur.next; } return map.get(head); }}整体代码应用举例:
// 借助链表中的引用次序进行存储 //需要自己定义一个节点类进行存储//节点类class ListNode { public int data; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; }}class MySingleList { public ListNode head;//标志头 public MySingleList() { this.head = null; } 1 头插法 public void addFirst(int data){ ListNode node = new ListNode(data); if(this.head == null) { this.head = node; }else { node.next = this.head; this.head = node; } } 2 尾插法 public void addLast(int data) { ListNode node = new ListNode(data); ListNode cur = this.head; //0、判断是否是第一次插入 if(this.head == null) { this.head = node; }else { //1、找尾巴 while (cur.next != null) { cur = cur.next; } //2、进行插入 cur.next = node; } } /** * 找到index-1位置的节点 返回当前节点的引用 * @param index * @return */ //找前驱 private ListNode searchIndex(int index) { //prev-->index-1; ListNode prev = this.head; int count = 0; while (count < index-1) { prev = prev.next; count++; } return prev; } 3 插入到index位置 //任意位置插入,第一个数据节点为0号下标 public boolean addIndex(int index,int data){ //下标不合法 if(index < 0 || index > getLength()) { return false; } //头插法 if(index == 0) { addFirst(data); return true; } ListNode prev = searchIndex(index); ListNode node = new ListNode(data); node.next = prev.next; prev.next = node; return false; } 4 返回链表长度 public int getLength() { int count = 0; ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { count++; cur = cur.next; } return count; } 5 打印单链表数据 public void display(){ if(this.head == null) { return; } ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { System.out.print(cur.data+" "); cur = cur.next; } System.out.println(); } 6 查找是否包含关键字key是否在单链表当中 public boolean contains1(int key){ ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if(cur.data == key) { return true; } cur = cur.next; } return false; } public ListNode contains2(int key){ ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if(cur.data == key) { return cur; } cur = cur.next; } return null; } //返回对应值节点的前驱 private ListNode searchPrev(int key) { ListNode prev = this.head; while (prev.next != null) { if(prev.next.data == key) { return prev; } prev = prev.next; } return null; } 7 删除第一次出现关键字为key的节点 public void remove(int key){ //1、删除的节点如果是头结点 if(this.head.data == key) { this.head = this.head.next; return; } //2、找到删除的节点的前驱 如果找不到 返回null ListNode prev = searchPrev(key); if(prev == null) { System.out.println("没有你要删除的节点"); return; } ListNode del = prev.next; //3、进行删除 prev.next = del.next; } 8 删除所有值为key的节点 public void removeAllKey(int key){ ListNode prev = this.head; ListNode cur = this.head.next; while (cur != null) { if(cur.data == key) { prev.next = cur.next; cur = cur.next; }else { prev = cur; cur = cur.next; } } if(this.head.data == key) { this.head = this.head.next; } } 9 清空链表 public void clear(){ //this.head = null; while (this.head.next != null) { ListNode cur = this.head.next; this.head.next = cur.next; } this.head = null; } 10 反转单链表 时间复杂度为O(N),只遍历了一遍单链表 public ListNode reverseList() { ListNode prev = null; ListNode cur = this.head; ListNode newHead = null; while (cur != null) { ListNode curNext = cur.next; if(curNext == null) { newHead = cur; } cur.next = prev; prev = cur; cur = curNext; } return newHead; } 11 打印反转后的单链表,要重写display public void display2(ListNode newHead){ if(newHead == null) { return; } ListNode cur = newHead; while (cur != null) { System.out.print(cur.data+" "); cur = cur.next; } System.out.println(); } 12 返回中间节点 public ListNode middleNode() { ListNode low = this.head; ListNode fast = this.head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null){ // fast = fast.next.next; //当fast遍历完时,low正好位于中间位置,因low比fast慢一半 low = low.next; } return low; } 13 返回倒数第K个节点 public ListNode findKthToTail(int k) { if(k <= 0) { return null; } ListNode fast = this.head; ListNode slow = this.head; while (k-1 > 0) { if(fast.next != null) { //加约束达成遍历一遍链表的目的 fast = fast.next; k--; }else { System.out.println("没有这个节点"); return null; } } while (fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next; slow = slow.next; } return slow; } 14 以x为基准分割链表 小于x的放在左边,大于等于x的都放在右边 public ListNode partition(int x){ ListNode bs = null; ListNode be = null; ListNode as = null; ListNode ae = null; ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur != null) { if(cur.data < x) { //是不是第一次插入 if(bs == null) { bs = cur; be = bs; }else { be.next = cur; be = be.next; //bs.be 区间的端点 } }else { //是不是第一次插入 if(as == null) { as = cur; ae = cur; }else { ae.next = cur; ae = ae.next; } } cur = cur.next; } //第一个区间没有数据 if(bs == null) { return as; } be.next = as;//若as为空或as正常有值 if(as != null) { ae.next = null;//as不为空需将结尾置为null,没有此句会出现死循环 } return bs; //返回头节点 } 15 删除所有重复节点!!!!!!加入了一个辅助节点 (排序链表,只保留没有重复出现的节点) public ListNode deleteDuplication(){ if(this.head == null) { return null; } ListNode cur = this.head; ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1); //虚拟节点 ListNode tmp = newHead; while (cur != null) { //重复的节点 if(cur.next != null && cur.data == cur.next.data) { //每一次都需要判断cur.next while (cur.next != null &&cur.data == cur.next.data) { cur = cur.next; } cur = cur.next; }else { tmp.next = cur; tmp = tmp.next; cur = cur.next; } } //如果最后的节点是重复的,已经删除 // 那么就需要将tmp.next = null; tmp.next = null; return newHead.next; } 16 判断一个链表是否为回文结构 先找到中间节点,然后再反转后半部分,最后前后依次进行比较。 public boolean chkPalindrome() { //两种特殊情况 //没有节点 if(this.head == null) { return false; } //只有一个节点 if(this.head.next == null) { return true; } //1、找到单链表的中间节点 ListNode fast = this.head; ListNode slow = this.head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; } //循环结束后,slow即为中间节点 //2、反转单链表(反转中间节点的后半部分) ListNode cur = slow.next; while (cur != null) { ListNode curNext = cur.next; cur.next = slow; slow = cur; cur = curNext; } //3、fast/slow往前 head往后走 走到中间时会出现重合 while (slow != this.head) { // if(slow.data != this.head.data) { return false; } //增加判断偶数的情况 if(this.head.next == slow) { return true; } slow = slow.next; this.head = this.head.next; } return true; } 17 创造一个环 public void creteLoop() { ListNode cur = this.head; while (cur.next != null) { cur = cur.next; } cur.next = this.head.next.next; } 18 判断一个链表是否有环 public boolean hasCycle(){ ListNode fast = this.head; ListNode slow = this.head; while (fast != null && fast.next!= null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if(slow == fast) { return true; } } return false; } 19 返回入环节点 (相遇之后,slow从头节点开始走,fast从相遇处开始走, 当再次相遇时即为入环节点。) public ListNode detectCycle() { ListNode fast = this.head; ListNode slow = this.head; while (fast != null && fast.next!= null) { fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if(slow == fast) { break; } } if(fast == null || fast.next == null) { return null;//无环 } //有环 slow = this.head; while (slow != fast) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; }}测试:
public class TestSingleList { 20 将两个有序单链表 合并称为一个新的有序链表 并返回 public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode headA, ListNode headB){ ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1); ListNode tmp = newHead; while (headA != null && headB != null) { if(headA.data < headB.data) { tmp.next = headA; headA = headA.next; tmp = tmp.next; }else { tmp.next = headB; headB = headB.next; tmp = tmp.next; } } if (headA != null) { tmp.next = headA; } if(headB != null) { tmp.next = headB; } return newHead.next; } 21 判断两个单链表是否有交点 public static ListNode getIntersectionNode (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { if(headA == null || headB == null) { return null; } ListNode pL = headA;//永远指向长的单链表 ListNode pS = headB;//永远指向短的单链表 int lenA = 0; int lenB = 0; //求的lenA lenB while (pL != null) { lenA++; pL = pL.next; } while (pS != null) { lenB++; pS = pS.next; } //复位 pL = headA; pS = headB; //差值-》最长的单链表先走len步 int len = lenA-lenB; if(len < 0) { pL = headB; pS = headA; len = lenB-lenA; } //让pL先走len步 while (len > 0) { pL = pL.next; len--; } //开始一起走 (pL != pS ) {一人一步走} while (pL != pS) { pS = pS.next; pL = pL.next; } if(pL == null) { return null; } return pL; } //创建一个有交点的,单链表 public static void createCut (ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { headA.next = headB.next.next; } 22 复制带随机指针的链表 在OJ上做,OJ提供的ListNode有三个域 public ListNode copyRandomList(Node head) { if(head == null){ return null; } //1、老新进行进行交替链接 ListNode cur = head; while(cur != null) { ListNode node = new ListNode(cur.val,cur.next,null); Node tmp = cur.next; cur.next = node; cur = tmp; } // 2、修改random cur = head; while(cur != null) { if(cur.random != null) { cur.next.random = cur.random.next; cur = cur.next.next; }else{ cur = cur.next.next; } } //3、将老新节点 打开 cur = head; ListNode newHead = cur.next; while(cur.next != null) { ListNode tmp = cur.next; cur.next = tmp.next; cur = tmp; } return newHead; }} public static void main(String[] args) { MySingleList mySingleList = new MySingleList(); mySingleList.addIndex(0,199); mySingleList.addLast(1); mySingleList.addLast(2); mySingleList.addLast(3); mySingleList.addLast(4); mySingleList.addLast(5); mySingleList.display(); //逆置 System.out.println("逆置"); ListNode newhead = mySingleList.reverseList(); mySingleList.display2(newhead); //返回中间节点 ListNode node = mySingleList.middleNode(); System.out.println(node.data); //返回倒数第K个节点 ListNode node1 = mySingleList.findKthToTail(1); System.out.println(node1.data); //以x为基准划分区间 ListNode head = mySingleList.partition(3); //划分区间后,有一个新的头,需要调用display2 mySingleList.display2(head); //删除重复节点 ListNode newhead1 = mySingleList.deleteDuplication(); mySingleList.display2(newhead1); //判断是否为回文结构 boolean flg = mySingleList.chkPalindrome(); System.out.println(flg); //创造一个环 mySingleList.creteLoop(); //判断是否为环结构 boolean flg1 = mySingleList.hasCycle(); System.out.println(flg1); //连接两个链表 MySingleList mySingleList1 = new MySingleList(); mySingleList1.addLast(3); mySingleList1.addLast(3); mySingleList1.addLast(4); mySingleList1.addLast(5); mySingleList1.addLast(6); mySingleList1.addLast(7); mySingleList1.display(); MySingleList mySingleList2 = new MySingleList(); mySingleList2.addLast(1); mySingleList2.addLast(3); mySingleList2.addLast(2); mySingleList2.addLast(3); mySingleList2.addLast(6); mySingleList2.addLast(8); mySingleList2.display(); ListNode newhead2 = mergeTwoLists(mySingleList1.head,mySingleList2.head); mySingleList.display2(newhead2); //判断连个链表是否相交 //创建一个有交点的单链表 createCut(mySingleList1.head, mySingleList2.head); ListNode node2 = getIntersectionNode(mySingleList1.head, mySingleList2.head); System.out.println(node2.data); }}发表评论
最新留言
留言是一种美德,欢迎回访!
[***.207.175.100]2025年03月24日 01时05分03秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!