
设计模式之组合模式
发布日期:2021-05-07 15:14:42
浏览次数:7
分类:原创文章
本文共 2486 字,大约阅读时间需要 8 分钟。
目录
组合模式
概念
- Composite模式也叫组合模式,是构造型的设计模式之一。
- 通过递归手段来构造树形的对象结构,并可以通过一个对象来访问整个对象树。
角色和职责
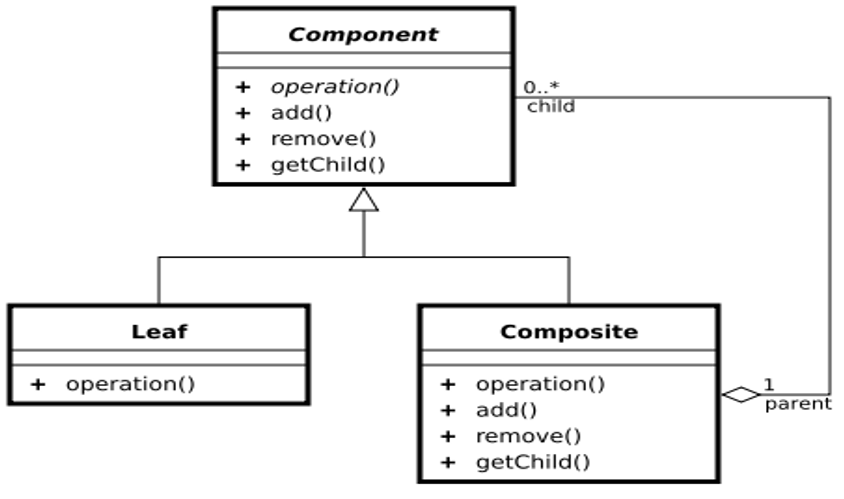
- Component (树形结构的节点抽象)
- - 为所有的对象定义统一的接口(公共属性,行为等的定义)
- - 提供管理子节点对象的接口方法
- - [可选]提供管理父节点对象的接口方法
- Leaf (树形结构的叶节点)
- Component的实现子类
- Composite(树形结构的枝节点)
- Component的实现子类
- 适用于:
- 单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性。将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分--整体”
案例
#include <iostream>using namespace std;#include "list"#include "string"//class IFile{public: virtual void display() = 0; virtual int add(IFile *ifile) = 0; virtual int remove(IFile *ifile) = 0; virtual list<IFile *>* getChild() = 0;protected:private:};class File : public IFile{public: File(string name) { m_list = NULL; m_name = ""; m_name = name; } ~File() { if (m_list != NULL) { delete m_list; } } virtual void display() { cout << m_name << endl; } virtual int add(IFile *ifile) { return -1; } virtual int remove(IFile *ifile) { return -1; } virtual list<IFile *>* getChild() { return NULL; }private: list<IFile *> * m_list; string m_name;};class Folder : public IFile{public: Folder(string name) { m_name = name; m_list = new list<IFile *>; } ~Folder() { if (m_list == NULL) { delete m_list; } } virtual void display() { cout << m_name << endl; } virtual int add(IFile *ifile) { m_list->push_back(ifile); return 0; } virtual int remove(IFile *ifile) { m_list->remove(ifile); return 0; } virtual list<IFile *>* getChild() { return m_list; }private: list<IFile *> * m_list; string m_name;};void showTree(IFile *ifile, int level){ list<IFile *> *l = NULL; int i = 0; for (i=0; i<level; i++) { printf("\t"); } ifile->display(); l = ifile->getChild(); if (l != NULL) { for (list<IFile *>::iterator it=l->begin(); it!=l->end(); it++) { if ( (*it)->getChild() == NULL) { for (i=0; i<=level; i++) //注意 <= { printf("\t"); } (*it)->display(); } else { showTree((*it), level + 1); } } }}void main(){ Folder *root = new Folder("C:"); Folder *dir1 = new Folder("111dir"); File *txt1 = new File("aaa.txt"); Folder *dir12 = new Folder("222dir"); //dir12->display(); File *txt12 = new File("222.txt"); //txt12->display(); root->display(); root->add(dir1); root->add(txt1); dir1->add(dir12); dir1->add(txt12); /* list<IFile *> *l = dir1->getChild(); for (list<IFile *>::iterator it=l->begin(); it!=l->end(); it++) { (*it)->display(); } */ //开发一个递归函数 现在根结点下的所有子结点 cout << "测试递归函数" << endl; showTree(root, 0); delete txt12; delete dir12; delete dir1; delete txt1; delete root; cout<<"hello..."<<endl; system("pause"); return ;}【注】参考传智扫地僧C++设计模式
发表评论
最新留言
表示我来过!
[***.240.166.169]2025年04月03日 05时54分25秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
Factor Exposure因子暴露
2019-03-04
理解zvt in Python on Quant
2019-03-04
将DataFrame作为邮件正文HTML发送 in Python
2019-03-04
理解Python系统下的时间格式
2019-03-04
《经济机器是怎样运行的》笔记(三)
2019-03-04
prod()与cumprod()区别cumsum()
2019-03-04
Python提升回测速度concurrnet.futures模块详解
2019-03-04
Python语言'类'概念再理解
2019-03-04
(2019.6.27)Anaconda清华镜像已恢复使用
2019-03-04
Robomongo使用教程:踩着前辈的路
2019-03-04
Python中Class类与def函数的区别
2019-03-04
OpenAI Gym简介及初级实例
2019-03-04
用Matplotlib和Gym优雅地呈现股票交易智体
2019-03-04
Github上量化交易相关项目汇总
2019-03-04
JS取出两个数组中的不同或相同元素
2019-03-04
Ubuntu 18.04 zip压缩文件及其文件 夹中的所以 内容
2019-03-04
MFC:pic控件的矩形的left、right、top、bottom 坐标位置
2019-03-04