
本文共 5154 字,大约阅读时间需要 17 分钟。
作为数据结构的课程笔记,以便查阅。如有出错的地方,还请多多指正!
注:C++忘得太厉害了。。算法先用C实现,等之后复习了再改成C++
目录
- 有向无环图 / DAG图(directed acycline graph)
拓扑排序 Topological Sort
问题提出:学生选修课程问题
学生应按怎样的顺序学习这些课程,才能无矛盾、顺利地完成学业?
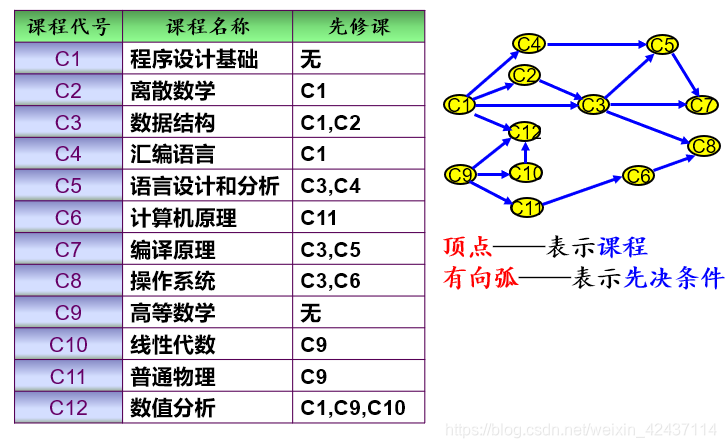
- AOV网——用顶点表示活动,用弧表示活动间优先关系的有向图称为顶点表示活动的网(Activity On Vertex network)
AOV网中不允许有回路,这意味着某项活动以自己为先决条件 - 拓扑排序——把AOV网络中各顶点按照它们相互之间的优先关系排列成一个线性序列
拓扑排序的方法
- 在有向图中选一个没有前驱的顶点且输出之
- 从图中删除该顶点和所有以它为尾的弧
- 重复上述两步,直至全部顶点均已输出;或者当图中不存在无前驱的顶点为止

检测AOV网中是否存在环方法:对有向图构造其顶点的拓扑有序序列,若网中所有顶点都在它的拓扑有序序列中,则该AOV网必定不存在环

算法实现
拓扑排序中,最常用的操作就是求邻接点和入度。因此以邻接表作为存储结构
- 额外设置一个数组来存储各个结点的入度,或者加入入度域

- 邻接表中所有入度为0的顶点进栈
- 栈非空时,栈顶元素 V V V出栈并输出到拓扑序列中;将 V V V的所有邻接顶点入度减1,若为0则进栈
重复上述操作直至栈空为止 - 若栈空时输出的顶点个数不是 n n n,则有向图有环;否则,拓扑排序完毕

输出序列:6 1 3 2 4 5
static void Calc_indegree(pAdjacentList_t pgraph, int indegree[]){ for (int i = 0; i < pgraph->vexNum; ++i) { indegree[i] = 0; } for (int i = 0; i < pgraph->vexNum; ++i) { pArcNode_t arc; for (arc = pgraph->vex[i].firstEdge; arc; arc = arc->nextEdge) { indegree[arc->head]++; } }}//拓扑排序int Topological_sort(pAdjacentList_t pgraph, void (*visit)(AdjacentListDataType_t data)){ int* indegree = (int*)malloc(pgraph->vexNum * sizeof(int)); pStackNode_t ptop; int cnt = 0;//输出的顶点个数 Calc_indegree(pgraph, indegree); Stack_init(&ptop); for (int i = 0; i < pgraph->vexNum; ++i) { if (0 == indegree[i]) { Push(&ptop, i); } } while (!Stack_is_empty(ptop)) { int i; pArcNode_t arc; Pop(&ptop, &i); visit(pgraph->vex[i].data); ++cnt; for (arc = pgraph->vex[i].firstEdge; arc; arc = arc->nextEdge) { if (0 == --indegree[arc->head]) { Push(&ptop, arc->head); } } } free(indegree); return (cnt == pgraph->vexNum);//是否有环}T ( n ) = O ( n + e ) T(n)=O(n+e) T(n)=O(n+e)
关键路径 Critical Path
问题提出
设一个工程有11项活动,9个事件
问题:(1) 完成整项工程至少需要多少时间? (2) 哪些活动是影响工程进度的关键?
把工程计划表示为有向图。每个事件表示在它之前的活动已完成,在它之后的活动可以开始

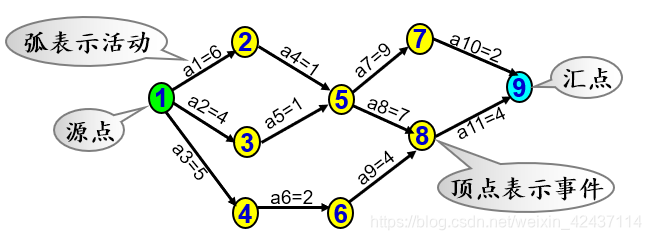
只有在不改变关键路径的前提下,提高所有关键路径上的公共活动的效率才能缩短整个工期
基本概念
- 完成整个工程的最短时间为:从有向图的源点到汇点的最长路径
- AOE网(Activity On Edge)。AOE网中顶点表示事件,弧表示活动,权表示活动持续时间
- 关键路径——路径长度最长的路径
- V e ( j ) V_e(j) Ve(j)——表示事件 V j V_j Vj的最早发生时间
- V l ( j ) V_l(j) Vl(j)——表示事件 V j Vj Vj的最迟发生时间(不影响工期)
- e ( i ) e(i) e(i)——表示活动 a i a_i ai的最早开始时间
- l ( i ) l(i) l(i)——表示活动 a i a_i ai的最迟开始时间(不影响工期)
- l ( i ) − e ( i ) l(i)-e(i) l(i)−e(i)——表示完成活动 a i a_i ai的时间余量
- 关键活动—— l ( i ) = e ( i ) l(i)=e(i) l(i)=e(i)的活动,由关键活动组成关键路径
问题分析
-
如何找 e ( i ) = l ( i ) e(i)=l(i) e(i)=l(i)的关键活动?
设活动 a i a_i ai用弧 < j , k > <j,k> <j,k>表示,其持续时间记为: d u t ( < j , k > ) dut(<j,k>) dut(<j,k>)
则有: e ( i ) = V e ( j ) e(i)=V_e(j) e(i)=Ve(j) , l ( i ) = V l ( k ) − d u t ( < j , k > ) l(i)=V_l(k)-dut(<j,k>) l(i)=Vl(k)−dut(<j,k>) -
如何求 V e ( j ) V_e(j) Ve(j)和 V l ( j ) V_l(j) Vl(j)?
(1) 从 V e ( 1 ) = 0 V_e(1)=0 Ve(1)=0开始从前向后递推(拓扑有序)

(2)从 V l ( n ) = V e ( n ) V_l(n)=V_e(n) Vl(n)=Ve(n)开始从后向前递推(逆拓扑有序)

-
求关键路径步骤
求 V e ( i ) V_e(i) Ve(i)
求 V l ( j ) V_l(j) Vl(j)
求 e ( i ) = V e ( j ) e(i) =V_e(j) e(i)=Ve(j)
求 l ( i ) = V l ( k ) − d u t ( < j , k > ) l(i) =V_l(k)-dut(<j,k>) l(i)=Vl(k)−dut(<j,k>)
计算 l ( i ) − e ( i ) l(i)-e(i) l(i)−e(i)
算法实现
- 使用邻接表,增设入度域(或者一个记录各个结点入度的数组)
- 计算每个顶点的入度
- 对各个顶点进行拓扑排序,排序过程中求 V e ( i ) V_e(i) Ve(i)。将得到的拓扑序列入栈,以便之后得到逆拓扑序列
- 按逆拓扑序列求 V l ( i ) V_l(i) Vl(i)
- 计算每条弧(活动)的 e [ i ] e[i] e[i]和 l [ i ] l[i] l[i],找出 e [ i ] = l [ i ] e[i]=l[i] e[i]=l[i]的关键活动
//求图上的关键路径Status_e Critical_path(pAdjacentList_t pgraph){ int* indegree = (int*)malloc(pgraph->vexNum * sizeof(int)); AdjacentListWeightType_t* ve = (AdjacentListWeightType_t*)malloc(pgraph->vexNum * sizeof(AdjacentListWeightType_t)); AdjacentListWeightType_t* vl = (AdjacentListWeightType_t*)malloc(pgraph->vexNum * sizeof(AdjacentListWeightType_t)); AdjacentListWeightType_t ee; AdjacentListWeightType_t el; pStackNode_t ptop; int cnt = 0;//输出的顶点个数 pStackNode_t ptop_topological;//记录拓扑排序的次序 方便之后按逆序操作 int finish_time = 0; Calc_indegree(pgraph, indegree); Stack_init(&ptop); Stack_init(&ptop_topological); //入度为0的点入栈 for (int i = 0; i < pgraph->vexNum; ++i) { if (0 == indegree[i]) { Push(&ptop, i); } ve[i] = 0; vl[i] = INFINITY; } //栈不为空时,拓扑排序 while (!Stack_is_empty(ptop)) { int i; pArcNode_t arc; Pop(&ptop, &i); Push(&ptop_topological, i); ++cnt; for (arc = pgraph->vex[i].firstEdge; arc; arc = arc->nextEdge) { ve[arc->head] = MAX(ve[i] + arc->weight, ve[arc->head]); if (0 == --indegree[arc->head]) { Push(&ptop, arc->head); } finish_time = MAX(finish_time, ve[arc->head]); } } if (cnt < pgraph->vexNum) { printf("There is loop in the graph!\r\n"); return err; } else { printf("Project time:%d\n", finish_time); } while (!Stack_is_empty(ptop_topological)) { int i; pArcNode_t arc; Pop(&ptop_topological, &i); arc = pgraph->vex[i].firstEdge; if (NULL == arc) { vl[i] = finish_time; } for (; arc; arc = arc->nextEdge) { vl[i] = MIN(vl[arc->head] - arc->weight, vl[i]); } } printf("Critical path:\r\n"); for (int i = 0; i < pgraph->vexNum; ++i) { pArcNode_t arc; for (arc = pgraph->vex[i].firstEdge; arc; arc = arc->nextEdge) { ee = ve[i]; el = vl[arc->head] - arc->weight; if (ee == el) { printf("%d -> %d ( weight: %d ; ee/el : %d )\r\n", i, arc->head, arc->weight, ee); } } } free(indegree); free(ve); free(vl); return ok;}T ( n ) = O ( n + e ) T(n)=O(n+e) T(n)=O(n+e)
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
