linux 多线程同步 2019.1.9(互斥量的使用,死锁,读写锁,条件变量,信号量,文件锁)
发布日期:2021-05-06 23:06:36
浏览次数:38
分类:精选文章
本文共 7609 字,大约阅读时间需要 25 分钟。
学习目标

互斥量的使用
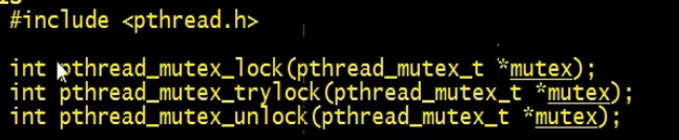
lock和unlock的使用例子
通过互斥量,两个线程交替打印
#include#include #include #include //常量初始化锁——mutex(这样就不用init函数了),将其定义为全局变量pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;int sum=0;void *thr1(void *arg){ while(1){ //先上锁 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); printf("hello"); sleep(rand()%3); printf("world\n"); //释放锁 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); sleep(rand()%3); }}void *thr2(void *arg){ while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); printf("HELLO"); sleep(rand()%3); printf("WORLD\n"); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); sleep(rand()%3); }}int main(){ pthread_t tid[2]; pthread_create(&tid[0],NULL,thr1,NULL); pthread_create(&tid[1],NULL,thr2,NULL); pthread_join(tid[0],NULL); pthread_join(tid[1],NULL); return 0;}
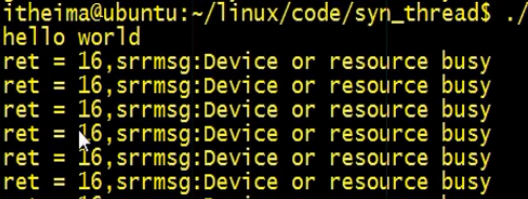
trylock
![]()
#include#include #include #include pthread_mutex_t mutex;void *thr(void *arg){ while(1){ pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); printf("hello world\n"); sleep(30); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); } return NULL;}int main(){ pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL); pthread_t tid; pthread_create(&tid,NULL,thr,NULL); sleep(1); while(1){ int ret = pthread_mutex_trylock(&mutex); //加锁失败 if(ret > 0){ printf("ret = %d,srrmsg:%s\n",ret,strerror(ret)); } sleep(1); } return 0;}
返回值的错误码是16,我们来看一下16代表什么意思。
错误码定义的地方

死锁
产生条件
- 锁了又锁,自己加了锁,自己又加了一把锁。一般都是有分支或者写代码的时候忘了会出现这个问题
- 交叉锁(如下图所示)——解决方案:1、每个线程申请锁的顺序要一致;2、如果申请到一把锁,另一个申请不到,则释放已有资源
互斥量只是建议锁

读写锁
读共享,写互斥,写的优先级高。适合读的线程多的场景
读写锁仍然是一把锁,有不同的状态:
- 未加锁
- 读锁
- 写锁
读写锁练习场景


初始化
一种初始化的方式

另一种初始化的方式
![]()
销毁读写锁

读写锁的例子
#include#include #include //初始化pthread_rwlock_t rwlock = PTHREAD_RWLOCK_INITIALIZER;int beginnum = 1000;void *thr_write(void *arg) { while(1){ //写锁加锁 pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock); printf("---%s---self---%lu---beginnum---%d\n",__FUNCTION__,pthread_self(),++beginnum); usleep(2000);//模拟占用时间 //解锁 pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); usleep(4000); } return NULL;}void *thr_read(void *arg) { while(1){ //读锁加锁 pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&rwlock); printf("---%s---self---%lu---beginnum---%d\n",__FUNCTION__,pthread_self(),beginnum); usleep(2000);//模拟占用时间 //解锁 pthread_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock); usleep(2000); } return NULL;}int main(){ //创建5个读锁和3个写锁 int n =8,i = 0; pthread_t tid[8];//5-read ,3-write for(i = 0; i < 5; i ++){ //参数依次是线程地址、线程属性、函数名、传入的参数 pthread_create(&tid[i],NULL,thr_read,NULL); } for(;i < 8; i ++){ //参数依次是线程地址、线程属性、函数名、传入的参数 pthread_create(&tid[i],NULL,thr_write,NULL); } for(i = 0; i < 8;i ++){ //线程回收 pthread_join(tid[i],NULL); } return 0;}
条件变量
引入原因:mutex会产生如下问题
多个线程抢到锁之后,发现并没有资源,因此释放锁,然后继续多线程抢锁,然后释放锁,这户造成资源的浪费。
三个吃货抢锁,抢到的人打开饼筐发现没有饼,于是释放锁,然后三个吃货继续抢锁。

条件变量可以引起阻塞,并非锁,要和互斥变量组合使用
超时等待

传入参数中的timespec结构体:


条件变量阻塞等待


使用条件变量解决问题的例子
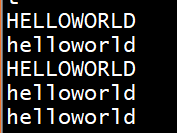
两个线程,一个线程想把所有的内容都写成0,另一个线程想把所有的内容都写成1
#include#include #include #include #include #include #include #include pthread_mutex_t mutex ;char buf[20];void *thr1(void *arg){ int i = 0 ; //加锁 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); for(;i< 20; i ++){ usleep(rand()%3); buf[i] = '0'; } //解锁 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); return NULL;}void *thr2(void *arg) { int i = 0 ; //加锁 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); for (; i < 20; i++) { usleep(rand() % 3); buf[i] = '1'; } //解锁 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); return NULL;}int main(){ //两个线程,一个线程想把所有的内容都写成0,另一个线程想把所有的内容都写成1 memset(buf,0x00,sizeof(buf)); //初始化条件变量 pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL); pthread_t tid[2]; pthread_create(&tid[0],NULL,thr1,NULL); pthread_create(&tid[1],NULL,thr2,NULL); pthread_join(tid[0],NULL); pthread_join(tid[1],NULL); printf("buf is %s\n",buf); //释放条件变量 pthread_mutex_destory(&mutex); return 0;}
条件变量解决生产着消费者模型
一个生产者一个消费者时
用链表存储数据
#include#include #include #include int beginnum = 1000;//初始化mutexpthread_mutex_t mutex=PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;//初始化条件变量pthread_cond_t cond=PTHREAD_COND_INITIALIZER;typedef struct _ProdInfo{ int num; struct _ProdInfo *next;}ProdInfo;ProdInfo *HEAD = NULL;void *thr_producer(void *arg){ //负责向链表添加数据 while(1){ ProdInfo *prod=malloc(sizeof(ProdInfo)); prod->num=beginnum++; //上锁 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); //add to list prod->next=HEAD; HEAD=prod; printf("--------%s--------seld=%lu------------%d\n",__FUNCTION__,pthread_self(), prod->num); pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); //发起通知 pthread_cond_signal(&cond); sleep(rand()%4); } return NULL;}void *thr_customer(void *arg){ ProdInfo *prod=NULL; while(1){ //取链表的数据 pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex); //判断有没有数据 if(HEAD==NULL){ //发送消息等待 pthread_cond_wait(&cond, &mutex); } //此时链表非空 prod=HEAD; HEAD=HEAD->next; printf("--------%s--------seld=%lu------------%d\n",__FUNCTION__,pthread_self(), prod->num); //解锁 pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex); sleep(rand()%4); free(prod); } return NULL;}int main(){ pthread_t tid[2]; pthread_create(&tid[0], NULL, thr_producer, NULL); pthread_create(&tid[1], NULL, thr_customer, NULL); pthread_join(tid[0], NULL); pthread_join(tid[1], NULL); pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex); pthread_cond_destroy(&cond); return 0;}

一个生产者多个消费者时
把thr_customer中的
if(HEAD==NULL)
改成
while(HEAD==NULL)
即可。
信号量
加强版的互斥锁。适于多个资源多个线程访问的情况。


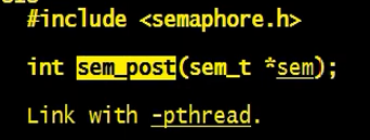
初始化
![]()
- sem 定义的信号量,传出
- pshared 非0则代表进程信号量, 0代表线程信号量
- value 定义信号量的并发数(钥匙的个数)
摧毁信号量
![]()
申请信号量,申请成功,则value--

释放信号量 value++
![]()
信号量实现生产者消费者模型
#include#include #include #include #include //blank只有多少可以放生产者生产东西的地方,xfull是消费者可以消费的东西的数量sem_t blank,xfull;#define _SEM_CNT_ 5// 模拟饼筐int queue[_SEM_CNT_];int beginnum = 100;void *thr_producter(void *arg) { int i = 0; while(1){ //申请资源 blank-- //看看能不能生产,还有没有空间 sem_wait(&blank); //打印函数名、线程名、数量 printf("-----%s-----self--%lu----num----%d\n",__FUNCTION__,pthread_self(),beginnum); //生产数据 queue[(i++)%_SEM_CNT_] = beginnum++; //xfull ++ sem_post(&xfull); sleep(rand()%3); } return NULL;}void *thr_customer(void *arg) { int i = 0; int num = 0; while(1){ //看看能不能消费 sem_wait(&xfull); //通过取余来 num = queue[(i++)%_SEM_CNT_]; printf("-----%s-----self--%lu----num----%d\n",__FUNCTION__,pthread_self(),num); //发送信号 sem_post(&blank); sleep(rand()%3); } return NULL;}int main(){ //线程,所有第二个参数是0, 如果是进程,则第二个参数是非0 sem_init(&blank,0,_SEM_CNT_); //消费者一开始的初始化默认没有产品 sem_init(&xfull,0,0); pthread_t tid[2]; //线程没有设置属性,所有第二个参数为NULL pthread_create(&tid[0],NULL,thr_producter,NULL); pthread_create(&tid[1],NULL,thr_customer,NULL); pthread_join(tid[0],NULL); pthread_join(tid[1],NULL); sem_destroy(&blank); sem_destroy(&xfull); return 0;}
文件锁

适合环境——当前系统中该进程只能起一个。
实现原理——当一个进程打开了这个文件,另一个进程发现文件被打开了,就无法再打开这个文件了。
文件锁——读共享,写独占
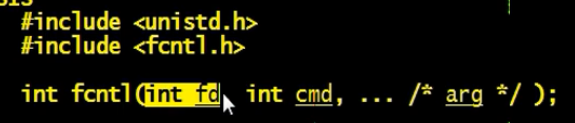
#include#include #include #include #include #include #define _FILE_NAME_ "/home/itheima/temp.lock"int main() { int fd = open(_FILE_NAME_,O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0666); if(fd < 0){ //文件打开失败 perror("open err"); return -1; } struct flock lk; lk.l_type = F_WRLCK; lk.l_whence =SEEK_SET ; lk.l_start = 0; lk.l_len =0; if(fcntl(fd,F_SETLK,&lk) < 0){ perror("get lock err"); exit(1); } // 核心逻辑 while(1){ printf("I am alive!\n"); sleep(1); } return 0;}
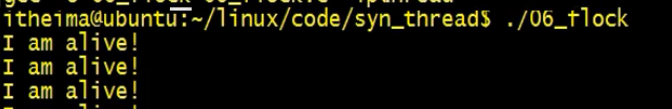
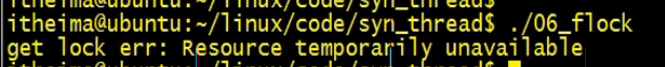
哲学家用餐问题

发表评论
最新留言
做的很好,不错不错
[***.243.131.199]2025年04月02日 23时10分09秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
JMeter 中实现发送Java请求
2021-05-09
设计模式点滴
2021-05-09
数据库优化
2021-05-09
[备忘]域用户登陆出现“此工作站和主域间的信任关系失败”错误解决方法
2021-05-09
继续聊WPF——用Blend自定义Listview控件的列表头
2021-05-09
【.net 深呼吸】启动一个进程并实时获取状态信息
2021-05-09
OO_Unit2 多线程电梯总结
2021-05-09
json-lib的使用《二》
2021-05-09
LeetCode52题,别再问我N皇后问题了
2021-05-09
简单实用算法——字节位序反转
2021-05-09
webpack之带有可自动打开浏览器及热重载的基本配置
2021-05-09
前端的批量接口如何快速响应?有没有通用解决方案?
2021-05-09
Shader 入门笔记(一) 如何学习shader
2021-05-09
Huffman树及其编解码
2021-05-09
分布式、高并发、高性能场景(抢购、秒杀、抢票、限时竞答)数据一致性解决方案
2021-05-09
20.波利亚过程
2021-05-09
04_Mysql配置文件(重要参数)
2021-05-09
浅谈使用git进行版本控制
2021-05-09
python 序列化及其相关模块(json,pickle,shelve,xml)详解
2021-05-09