本文共 10811 字,大约阅读时间需要 36 分钟。
有查询条件就查询,
多个查询条件,只要有查询,就增加一个查询条件
一、TP5.1版本
模糊查询
$where[] = ['title','like',"%".$sotitle."%"];$map[] = ['name','like','think'];$map[] = ['status','=',1];//时间查询$wheret2[]= ['time','between',[$datatime1,$datatime2]];注意:$where[] = ['exp',Db::raw("FIND_IN_SET($id,category)")];//category值为数字,一但用到$where[]方式和where('type',1)不能同时存在一个语句中下面这语句的其它条件全部失效正确写:$where = "FIND_IN_SET($category_id,category)";$crs=Db::name('product')->field('id,title')->where('type',1)->where('type_mold',1)->where('deleted',0)->whereLike('title',"%".$sotitle."%")->where($where)->select()
in查询
$where1 = [ ['role_id', 'in', '1,2,3'], ];
TP5.1.21 版本之后数组查询支持:
要达到这样子查询:
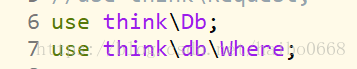
1、首先引用: use think\db\Where;
2、定义数组:$where = new Where;
3、就可以用了:$where['title'] = ['like', "%".$sotitle."%"];
->where('name','like',"%".$sotitle."%") $cid_al=array(1) { [0] => string(3) "879" [1] => string(3) "878"}$where['class_id'] = ['in', '$cid_all'];$where['id'] = ['in', $cid_al];//或这样子in可以直接这样子,$cid_all是一维数组$wherer['class_id'] = $cidarr;一样子效果:`class_id` IN (879,878)$where['title'] = ['like', '%php%'];$where['u.name|u.tel|u.real_name|u.nickname'] = ['like',"%".$keyword."%"];$where['id'] = ['<>', $id];$where['id'] = ['notin', $all_user_id];//不等于$where['number'] = ['=', null];//等空值where('','exp',Db::raw("FIND_IN_SET($pid,pc.pidarr)"))->join('menu m','find_in_set(m.id,b.category)!=0')$where2 = "FIND_IN_SET($category,c.category)";>where($where2)//值为数字$id=419;$where[] = ['exp',Db::raw("FIND_IN_SET($id,category)")];//category值为数字,例子:419,415,414//值为字符串$id值等于dfd 要注意'引号$where[] = ['exp',Db::raw("FIND_IN_SET('$id',category)")];//category值为数字,例子:'349/417/419','349/413/415','349/413/416'$where[]与$where['xx']不能同时存在 ->where("tp.id='".$id."' and tp.deleted=0")Db::table('think_user') ->where('id > 0 AND name LIKE "thinkphp%"') ->select(); 更多教程:
另一种方式:
if($sotitle){ if($sotype=="id"){ $where[$sotype] = $sotitle; }else{ $where = [ ['title', 'like', "%".$sotitle."%"], ]; } } $where['level'] = 1; $rs1=Db::name('column')->where($where)->select();
数组与时间一起查询
$rst=Db::name('order')->where($datac)->where('time', '<', $nowtimg)->setField('state', 2); // 查询有效期内的活动Db::name('event') ->whereTime('start_time', '<=', time()) ->whereTime('end_time', '>=', time()) ->select(); 时间查询另一个例子:
SELECT `id`,`starttime`,`endtime` FROM `edu_live_course` WHERE `pid` = 231 AND `level` = 2 AND ( starttime > "2018-11-22 18:24:11" or (starttime < "2018-11-22 18:24:11" and endtime > "2018-11-22 18:24:11") ) ORDER BY `starttime` ASC LIMIT 1
$ndate = date("Y-m-d H:i:s"); $rs_ccid=Db::name('live_course') ->field('id,starttime,endtime') ->where(['pid'=>$id,'level'=>2]) ->where('starttime > "'.$ndate.'" or (starttime < "'.$ndate.'" and endtime > "'.$ndate.'")') ->order('starttime', 'asc') ->find(); $ccid = $rs_ccid['id']; // echo Db::name('live_course')->getLastSql(); //dump($rs_ccid); FIND_IN_SET用法:
if($role_id==3){//老师 //$where['p.teachers_id']=$uid; $where .="p.teachers_id = ".$uid; }else{//1教务/助教 2班主任 } if($category){ //$where2[] = ['exp',Db::raw("FIND_IN_SET('$category',p.category)")]; $where .= ($where?' and ':'')." FIND_IN_SET('$category',p.category)"; } Db::name('menu')->where('FIND_IN_SET(:id,pid_all)',['id' => $id])->update([$field => $title]);->join('menu m','find_in_set(m.id,b.category)!=0')具体例子: if(count($allpid)>0){ $where1 = 'p.teachers_id='.$uid; //项目分类 if($category){// dump($category);die; //$categoryarr = implode(",",$categoryarr); //dump($categoryarr);die;// $where2[] = ['exp',Db::raw("FIND_IN_SET($category,c.category)")]; $where2 = "FIND_IN_SET($category,c.category)"; //dump($where); } foreach($allpid as $key => $v){ $pid=$v['id']; $rs = Db::name('register_module_pro_city') ->alias('pc') ->field('c.id,c.title') ->join('register_module m','pc.module_id = m.id') ->join('register_exa_date ed','find_in_set(m.id,ed.module_id)!=0') ->join('register_class c','find_in_set(ed.id,c.exa_date_id)!=0') ->join('product p','find_in_set(p.id,pc.pidarr)!=0') ->where('','exp',Db::raw("FIND_IN_SET($pid,pc.pidarr)"))// ->where($where) ->where($where1) ->where($where2) ->where('ed.deleted',0) ->where('c.deleted',0) ->where('m.deleted',0) ->where('pc.deleted',0) ->where('p.deleted',0) ->select(); //echo Db::name('register_module_pro_city')->getLastSql(); if(count($rs)>0){ foreach($rs as $k => $v1){ $allcid[$k]['cid'] =$v1['id']; $allcid[$k]['title'] =$v1['title']; } } $pid=''; } 5.1的数组查询方式有所调整,是为了尽量避免数组方式的条件查询注入。
如果需要事先组装数组查询条件,可以使用:
$map[] = ['name','like','think'];$map[] = ['status','=',1];
官方文档:https://www.kancloud.cn/manual/thinkphp5_1/354006
注意,
V5.1.7+版本数组方式如果使用exp查询的话,一定要用raw方法。
Db::table('think_user') ->where([ ['name', 'like', 'thinkphp%'], ['title', 'like', '%thinkphp'], ['id', 'exp', Db::raw('>score')], ['status', '=', 1], ]) ->select(); 数组查询方式,确保你的查询数组不能被用户提交数据控制,用户提交的表单数据应该是作为查询数组的一个元素传入,如下:
Db::table('think_user') ->where([ ['name', 'like', $name . '%'], ['title', 'like', '%' . $title], ['id', '>', $id], ['status', '=', $status], ]) ->select(); 注意,相同的字段的多次查询条件可能会合并,如果希望某一个
where方法里面的条件单独处理,可以使用下面的方式,避免被其它条件影响。
$map = [ ['name', 'like', 'thinkphp%'], ['title', 'like', '%thinkphp'], ['id', '>', 0], ];Db::table('think_user') ->where([ $map ]) ->where('status',1) ->select(); 生成的SQL语句为:
SELECT * FROM `think_user` WHERE ( `name` LIKE 'thinkphp%' AND `title` LIKE '%thinkphp' AND `id` > 0 ) AND `status` = '1'
如果使用下面的多个条件组合
$map1 = [ ['name', 'like', 'thinkphp%'], ['title', 'like', '%thinkphp'], ]; $map2 = [ ['name', 'like', 'kancloud%'], ['title', 'like', '%kancloud'], ]; Db::table('think_user') ->whereOr([ $map1, $map2 ]) ->select(); 生成的SQL语句为:
SELECT * FROM `think_user` WHERE ( `name` LIKE 'thinkphp%' AND `title` LIKE '%thinkphp' ) OR ( `name` LIKE 'kancloud%' AND `title` LIKE '%kancloud' )
善用多维数组查询,可以很方便的拼装出各种复杂的SQL语句
引用:https://www.kancloud.cn/manual/thinkphp5_1/354030
二、TP5.0版本
//类型 if($sotype){ $where['type'] = $sotype; } //合作单位 if($companyid){ $where['hezuodanwei'] = $companyid; } //关键词 模糊查询 $type 是变量 if($key){ $where[$type] = ['like',"%".$key."%"]; } $rs=Db::name('student')->where($where)->order('id desc')->limit($limit)->page($page)->select(); $rs1=Db::name('student')->where($where)->select(); 查询一段时间的数据:
$where['time'] = array('between', array($starttime,$enttime));
$where['type'] = $sotype;
$where['hezuodanwei'] = $companyid;
$where["username"] = ['like',"%".$tag["kw"]."%"];//模糊查询
$where[]=['exp','FIND_IN_SET(2,needID)'];
例子:id in(1,5,8)
$where['hezuodanwei'] =array('in','10,12');
组成查询数组$where
where($where)
引用:http://blog.csdn.net/u010447573/article/details/47420063
Where 条件表达式格式为:
$map['字段名'] = array('表达式', '操作条件'); 其中 $map 是一个普通的数组变量,可以根据自己需求而命名。上述格式中的表达式实际是运算符的意义:
| TP运算符 | SQL运算符 | 例子 | 实际查询条件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| eq | = | $map['id'] = array('eq',100); | 等效于:$map['id'] = 100; |
| neq | != | $map['id'] = array('neq',100); | id != 100 |
| gt | > | $map['id'] = array('gt',100); | id > 100 |
| egt | >= | $map['id'] = array('egt',100); | id >= 100 |
| lt | < | $map['id'] = array('lt',100); | id < 100 |
| elt | <= | $map['id'] = array('elt',100); | id <= 100 |
| like | like | $map<'username'> = array('like','Admin%'); | username like 'Admin%' |
| between | between and | $map['id'] = array('between','1,8'); | id BETWEEN 1 AND 8 |
| not between | not between and | $map['id'] = array('not between','1,8'); | id NOT BETWEEN 1 AND 8 |
| in | in | $map['id'] = array('in','1,5,8'); | id in(1,5,8) |
| not in | not in | $map['id'] = array('not in','1,5,8'); | id not in(1,5,8) |
| and(默认) | and | $map['id'] = array(array('gt',1),array('lt',10)); | (id > 1) AND (id < 10) |
| or | or | $map['id'] = array(array('gt',3),array('lt',10), 'or'); | (id > 3) OR (id < 10) |
| xor(异或) | xor | 两个输入中只有一个是true时,结果为true,否则为false,例子略。 | 1 xor 1 = 0 |
| exp | 综合表达式 | $map['id'] = array('exp','in(1,3,8)'); | $map['id'] = array('in','1,3,8'); |
补充说明
- 同 SQL 一样,ThinkPHP运算符不区分大小写,eq 与 EQ 一样。
- between、 in 条件支持字符串或者数组,即下面两种写法是等效的:
$map['id'] = array('not in','1,5,8');$map['id'] = array('not in',array('1','5','8'));
exp 表达式
上表中的 exp 不是一个运算符,而是一个综合表达式以支持更复杂的条件设置。exp 的操作条件不会被当成字符串,可以使用任何 SQL 支持的语法,包括使用函数和字段名称。
exp 不仅用于 where 条件,也可以用于数据更新,如:
$Dao = M("Article");// 构建 save 的数据数组,文章点击数+1$data['id'] = 10;$data['counter'] = array('exp','counter+1');// 根据条件保存修改的数据$User->save($data);
官方查询语法:https://www.kancloud.cn/manual/thinkphp5/135182
查询表达式
| 版本 | 新增功能 |
|---|---|
| 5.0.9 | 比较运算增加闭包子查询支持 |
| 5.0.4 | 支持对同一个字段多次调用查询方法 |
查询表达式支持大部分的SQL查询语法,也是ThinkPHP查询语言的精髓,查询表达式的使用格式:
where('字段名','表达式','查询条件');whereOr('字段名','表达式','查询条件'); 表达式不分大小写,支持的查询表达式有下面几种,分别表示的含义是:
| 表达式 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| EQ、= | 等于(=) |
| NEQ、<> | 不等于(<>) |
| GT、> | 大于(>) |
| EGT、>= | 大于等于(>=) |
| LT、< | 小于(<) |
| ELT、<= | 小于等于(<=) |
| LIKE | 模糊查询 |
| [NOT] BETWEEN | (不在)区间查询 |
| [NOT] IN | (不在)IN 查询 |
| [NOT] NULL | 查询字段是否(不)是NULL |
| [NOT] EXISTS | EXISTS查询 |
| EXP | 表达式查询,支持SQL语法 |
| > time | 时间比较 |
| < time | 时间比较 |
| between time | 时间比较 |
| notbetween time | 时间比较 |
表达式查询的用法示例如下:
EQ :等于(=)
例如:
where('id','eq',100);where('id','=',100); 和下面的查询等效
where('id',100); 表示的查询条件就是 id = 100
NEQ: 不等于(<>)
例如:
where('id','neq',100);where('id','<>',100); 表示的查询条件就是 id <> 100
GT:大于(>)
例如:
where('id','gt',100);where('id','>',100); 表示的查询条件就是 id > 100
EGT:大于等于(>=)
例如:
where('id','egt',100);where('id','>=',100); 表示的查询条件就是 id >= 100
LT:小于(<)
例如:
where('id','lt',100);where('id','<',100); 表示的查询条件就是 id < 100
ELT: 小于等于(<=)
例如:
where('id','elt',100);where('id','<=',100); 表示的查询条件就是 id <= 100
[NOT] LIKE: 同sql的LIKE
例如:
where('name','like','thinkphp%'); 查询条件就变成 name like 'thinkphp%'
V5.0.5+版本开始,like查询支持使用数组
where('name','like',['%think','php%'],'OR'); [NOT] BETWEEN :同sql的[not] between
查询条件支持字符串或者数组,例如:
where('id','between','1,8'); 和下面的等效:
where('id','between',[1,8]); 查询条件就变成 id BETWEEN 1 AND 8
[NOT] IN: 同sql的[not] in
查询条件支持字符串或者数组,例如:
where('id','not in','1,5,8'); 和下面的等效:
where('id','not in',[1,5,8]); 查询条件就变成 id NOT IN (1,5, 8)
[NOT] IN查询支持使用闭包方式
[NOT] NULL :
查询字段是否(不)是Null,例如:
where('name', null);where('title','null');where('name','not null'); 如果你需要查询一个字段的值为字符串null或者not null,应该使用:
where('title','=', 'null');where('name','=', 'not null'); EXP:表达式
支持更复杂的查询情况 例如:
where('id','in','1,3,8'); 可以改成:
where('id','exp',' IN (1,3,8) '); exp查询的条件不会被当成字符串,所以后面的查询条件可以使用任何SQL支持的语法,包括使用函数和字段名称。