
本文共 13665 字,大约阅读时间需要 45 分钟。
点击下方“民工哥技术之路”,选择“设为星标”
回复“1024”获取独家整理的学习资料!

AppImage 是一种在 Linux 系统中用于分发便携式软件,且不需要超级用户权限来安装它们的格式。它还允许 Linux 的上游开发者来分发他们的程序而不用考虑不同 Linux 发行版间的区别。AppImage 的核心思想是一个文件即一个应用程序,每个 AppImage 都包含应用程序以及应用程序运行所需的所有文件。


AppImage 工具介绍
像 Linux 本身一样,AppImageKit 是开源的。
 适用于所有相当现代的 Linux 桌面发行版。
适用于所有相当现代的 Linux 桌面发行版。
简单
AppImage 的核心思想是:一个应用程序 = 一个文件。每个 AppImage 都包含应用程序以及应用程序运行所需的所有文件。换句话说,除了操作系统本身的基础组件,Appimage 不需要依赖包即可运行。
可靠
AppImage 格式是上游应用打包的理想选择,这意味着你可以直接从开发者那里获取软件,而不需要任何中间步骤,这完全符合开发者意图。非常迅速。
快速
AppImage 应用可以直接下载并且运行,无需安装,并且不需要 root 权限。
AppImage 工具对比
对比多种软件格式的优势和劣势!
与 deb 和 rpm 对比
优势
-
AppImage 格式的应用可跨发行版运行,传统格式不可用或比较难。
AppImage 格式不需要安装即可运行,可在 $HOME 分区运行,节省更分区空间。
AppImage 无需 root 权限,告别输入密码时代。
AppImage 包含应用依赖,可不受软件仓库制约,快速分发应用版本且不破坏系统依赖。
AppImage 提供多种打包方式,即可手动打包,也可脚本打包。
劣势
-
AppImage 格式会造成库的冗余且体积偏大,戏称为“系统安装了一万个 libc”。
AppImage 不受检查,如果有来源不明的人打包,可能会带来安全风险。
运行一个旧的 AppImage 软件所带的依旧是旧版本的依赖库,可能会带来风险。
与 snap 和 flatpak 对比
优势
-
AppImage 无需运行时,安装 snap 和 flatpak 软件安装其运行时。
AppImage 格式不需要安装即可运行,可在 $HOME 分区运行,节省更分区空间。
AppImage 无需 root 权限,告别输入密码时代。
AppImage 不需要软件仓库,当然也可以有,易于传播。
AppImage 对华人友好,包括官方网站和官方文档都已经有对应的中文支持。
劣势
-
没有沙箱机制。
没有商业公司支持,导致开发了十多年才具有影响力。
对某些定制化安装的发行版不友好,比如 gentoo、archlinux 等。
AppImage 目录结构
需要注意 AppImage 所需的文件以及目录结构!
使用 AppImage 系列工具的前提就是,你所编写的程序项目或者工具依赖格式必须符合 AppDir 的目录要求,大致目录结构如下所示。
AppDir└── AppRun└── your_app.desktop└── your_app.png└── usr ├── bin │ └── your_app ├── lib └── share ├── applications │ └── your_app.desktop └── icons └──└── └── your_app.png
AppRun 文件
-
必须要有
启动主负载应用程序
其中 AppRun 文件是程序的启动入口点文件,需要有可执行权限。
在 AppImageKit 项目中提供了一个 AppRun.c 的实现,但我们可以使用语言,比如 shell 的实现,也可以仅使用与主要可执行文件的符号链接。
your_app.desktop 文件
-
必须要有
类似于 Windows 系统的快捷方式,即双击即可运行。
我们这里的 [your_app].desktop 文件将显示在桌面上,可使用链接的方式存在。
编写的格式可以参考:https://specifications.freedesktop.org/desktop-entry- spec/latest/ar01s06.html 这个网站,最简单的方法就是找一个改吧改吧。
[Desktop Entry]Name=HypnosExec=hypnos %FIcon=hypnosType=ApplicationCategories=Audio;AudioVideo;Comment=Music Player and LibraryMimeType=inode/directory;audio/flac;Name[en]=HypnosTerminal=falseStartupNotify=trueNoDisplay=false
your_app.png 文件
-
非必须
提供程序软件包的桌面显示图案。
Version 文件
-
非必须
用于显示程序软件包所对应的版本信息。
appimagetool 命令使用
介绍 AppImage 工具的使用格式和常用命令参数。
打包命令使用
appimagetool 命令用于把现有的 AppDir 目录生成一个 AppImage 程序。
Usage: appimagetool [OPTION...] SOURCE [DESTINATION] - Generate, extract, and inspect AppImagesHelp Options: -h, --help Show help optionsApplication Options: -l, --list List files in SOURCE AppImage -u, --updateinformation Embed update information STRING; if zsyncmake is installed, generate zsync file -g, --guess Guess update information based on Travis CI or GitLab environment variables --bintray-user Bintray user name --bintray-repo Bintray repository --version Show version number -v, --verbose Produce verbose output -s, --sign Sign with gpg[2] --comp Squashfs compression -n, --no-appstream Do not check AppStream metadata --exclude-file Uses given file as exclude file for mksquashfs, in addition to .appimageignore. --runtime-file Runtime file to use --sign-key Key ID to use for gpg[2] signatures --sign-args Extra arguments to use when signing with gpg
打包文件使用
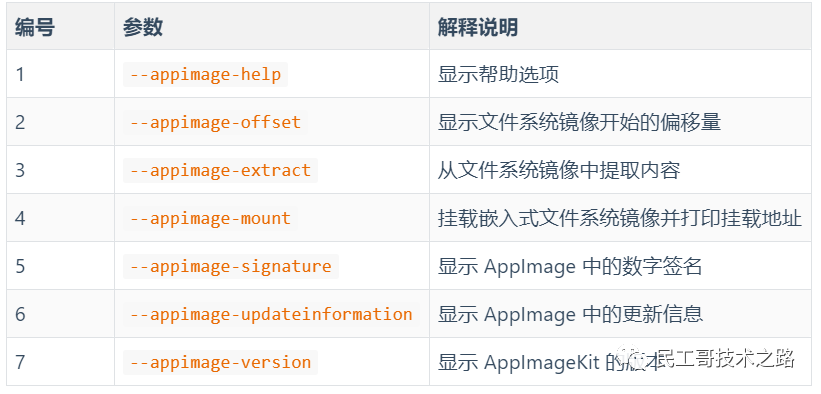
如果我们运行一个由 AppImageKit 工具构建的程序,那么其会附加以下参数,对应不同的参数会提供一些额外的特性和功能。
# usage./appimagetool-x86_64.AppImage some.AppDir
pkg2appimage 工具使用
pkg2appimage 工具适用于将 deb 格式的包变成 appimage 的独立可执行文件!
如果已经有了对应的二进制文件,不管是 zip 归档文件、.deb 格式的文件还是 ppa 源上的文件,我们只需要编写一个 .yml 格式的描述文件,然后使用 pkg2appimage 工具来运行它,就会帮助我们转换生成一个 AppImage 的独立文件,是不是非常简单呢?yml 描述文件告诉 pkg2appimage 从哪里获得所需要的内容,以及如何将它们转换为 AppImage。
# 执行方式$ bash -ex ./pkg2appimage recipes/XXX.yml
如果你只是看到了简答,那么你就太年轻了,你不知道这个 yml 格式的配置文件到底有多糟心。真的,看了官方文档中的配置文件介绍,以及对于官方仓库的示例软件对于 yml,心里有些懵逼。不过,等多看几次之后,就会发现还是不难写的,只是需要我们再出现错误的时候,能够及时调整配置文件,就可以正常打出我们需要的独立文件。
下面我们就一起看下,yml 文件的编写内容吧!正如我们所看到的那样,.yml 文件由三个部分组成,分别是主体部分、依赖部分和脚本部分。
app: zstd # 软件名称binpatch: true # chdir()overwrite: true # union file systemingredients: # 依赖关系;包的内容从哪里来 dist: bionic package: zstd sources: - deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ bionic main universescript: - cat > ./zstd.desktop <<\EOF - [Desktop Entry] - Type=Application - Terminal=true - Name=zstd - Exec=zstd - Icon=transmission-tray-icon.png - Categories=Development; - EOF - cat > ./AppRun <<\EOF - #!/bin/sh - HERE=$(dirname $(readlink -f "${0}")) - export LD_LIBRARY_PATH="${HERE}"/usr/lib:$PATH - "${HERE}"/usr/bin/zstd $@ - EOF - chmod a+x ./AppRun # 执行如下命令即可生成zstd的独立程序$ pkg2appimage ./zstd-appimage.yml
The overall p
-
必须存在
包含应用程序的名称
该名称必须与主入口文件的包名称匹配
app: zstd
The ingredients p
-
必须存在
描述如何获取进入 AppImage 的二进制内容
可包含 zip 归档文件、.deb 格式的文件还是 ppa 源上的文件
# Using ingredients from a binary archiveingredients: script: - DLD=$(wget -q "https://api.github.com/repos/atom/atom/releases/latest" -O - | grep -E "https.*atom-amd64.tar.gz" | cut -d'"' -f4) - wget -c $DLD - tar zxvf atom*tar.gz
# Using ingredients from a debian repositoryingredients: dist: xenial sources: - deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial main universe - deb http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/isv:/KDAB/xUbuntu_16.04/ /
# Using ingredients from an Ubuntu PPAingredients: dist: xenial sources: - deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial main universe ppas: - geany-dev/ppa
# Using local deb filesingredients: dist: xenial sources: - deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial main universe debs: - /home/area42/kdenlive.deb - /home/area42/kdenlive/*
# Excluding certain packagesingredients: dist: xenial packages: - multisystem - gksu sources: - deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial main universe - deb http://liveusb.info/multisystem/depot all main exclude: - qemu - qemu-kvm - cryptsetup - libwebkitgtk-3.0-0 - dmsetup
# Pretending certain versions of dependencies being installedingredients: dist: xenial sources: - deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial main universe ppas: - otto-kesselgulasch/gimp-edge pretend: - libcups2 1.7.2-0ubuntu1
# Arbitrary scripts in the ingredients pingredients: script: - URL=$(wget -q https://www.fosshub.com/JabRef.html -O - | grep jar | cut -d '"' -f 10) - wget -c "$URL" - wget -c --no-check-certificate --no-cookies --header "Cookie: oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u66-b17/jre-8u66-linux-x64.tar.gz
The script p
-
必须存在
脚本部分可能包含将二进制内容转换为适合于生成 AppImage 的 AppDir 所需的任意 shell 命令
# The script p needs to copy ingredients into placeingredients: dist: xenial sources: - deb http://archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial main universe script: - DLD=$(wget -q "https://github.com/feross/webtorrent-desktop/releases/" -O - | grep _amd64.deb | head -n 1 | cut -d '"' -f 2) - wget -c "https://github.com/$DLD"script: - mv opt/webtorrent-desktop/* usr/bin/ - sed -i -e 's|/opt/webtorrent-desktop/||g' webtorrent-desktop.desktop
# The script p needs to copy ingredients into placeingredients: script: - wget -c "https://telegram.org/dl/desktop/linux" --trust-server-names - tar xf tsetup.*.tar.xzscript: - cp ../Telegram/Telegram ./usr/bin/telegram-desktop
# The script p needs to copy icon and .desktop file in placescript: - tar xf ../fritzing* -C usr/bin/ --strip 1 - mv usr/bin/fritzing.desktop .
# The script p needs to copy icon and .desktop file in placescript: - # Workaround for: - # https://bugzilla.mozilla.org/show_bug.cgi?id=296568 - cat > firefox.desktop <
# The script p needs to copy icon and .desktop file in placescript: - cp ./usr/share/applications/FBReader.desktop fbreader.desktop - sed -i -e 's|Exec=FBReader|Exec=fbreader|g' fbreader.desktop - sed -i -e 's|Name=.*|Name=FBReader|g' fbreader.desktop - sed -i -e 's|Icon=.*|Icon=fbreader|g' fbreader.desktop - mv usr/bin/FBReader usr/bin/fbreader - cp usr/share/pixmaps/FBReader.png fbreader.png
下面示例是 pip 这个工具的官方仓库中给出的 yml 配置文件。
# Converting Python applications packaged with pipapp: mu.codewith.editoringredients: dist: xenial sources: - deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial xenial-updates xenial-security main universe - deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial-updates main universe - deb http://us.archive.ubuntu.com/ubuntu/ xenial-security main universe packages: - python3.4-venv script: - wget -c https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mu-editor/mu/master/conf/mu.codewith.editor.png - wget -c https://raw.githubusercontent.com/mu-editor/mu/master/conf/mu.appdata.xmlscript: - cp ../mu.codewith.editor.png ./usr/share/icons/hicolor/256x256/ - cp ../mu.codewith.editor.png . - mkdir -p usr/share/metainfo/ ; cp ../mu.appdata.xml usr/share/metainfo/ - virtualenv --python=python3 usr - ./usr/bin/pip3 install mu-editor - cat > usr/share/applications/mu.codewith.editor.desktop <<\EOF - [Desktop Entry] - Type=Application - Name=Mu - Comment=A Python editor for beginner programmers - Icon=mu.codewith.editor - Exec=python3 bin/mu-editor %F - Terminal=false - Categories=Application;Development; - Keywords=Python;Editor;microbit;micro:bit; - StartupWMClass=mu - MimeType=text/x-python3;text/x-python3; - EOF - cp usr/share/applications/mu.codewith.editor.desktop . - usr/bin/pip3 freeze | grep "mu-editor" | cut -d "=" -f 3 >> ../VERSION
下面示例是 Atom 这个代码编辑器官方仓库中给出的 yml 配置文件。
app: Atomingredients: script: - DLD=$(wget -q "https://api.github.com/repos/atom/atom/releases/latest" -O - | grep -E "https.*atom-amd64.tar.gz" | cut -d'"' -f4) - wget -c $DLD - echo $DLD | cut -d/ -f8 > VERSION - tar zxvf atom*tar.gzscript: - cp -r ../atom-*/* usr/bin/ - find . -name atom.png -exec cp {} atom.png \; - cat > atom.desktop <<\EOF - [Desktop Entry] - Type=Application - Name=Atom - Icon=atom - Exec=atom %u - Categories=Development;IDE; - Comment=The hackable text editor - EOF linuxdeployqt 工具使用
linuxdeployqt 是 Linux 下的 qt 打包工具!
工具安装
# 下载linuxdeployqt工具$ wget "https://github.com/probonopd/linuxdeployqt/releases/download/7/linuxdeployqt-7-x86_64.AppImage"# 重命名linuxdeployqt名称$ mv linuxdeployqt-continuous-x86_64.AppImage linuxdeployqt# 变成系统可执行文件$ sudo mv ./linuxdeployqt /usr/local/bin$ sudo chmod 755 linuxdeployqt# 查看linuxdeployqt版本$ sudo linuxdelpoyqt --versionlinuxdeployqt 4 (commit 988d294), build 481 built on 2018-02-02 15:05:23 UTC
# linuxdeployqt命令要用到-appImage选项$ wget -c "https://github.com/AppImage/AppImageKit/releases/download/12/appimagetool-x86_64.AppImage" -O /usr/local/bin/appimagetool# 变成系统可执行文件$ sudo chmod a+x /usr/local/bin/appimagetool
打包程序
# 不能定会成功$ linuxdeployqt <自己的工程名称> -appimage
官方文章中的示例演示
打包软件程序的简单演示流程 - cmake
生成 AppDir 打包目录
# fetch sources (you could as well use a tarball etc.)> git clone https://github.com/linuxdeploy/QtQuickApp.git> cd QtQuickApp# build out of source> mkdir build> cd build# configure build system# the flags below are the bare minimum that is needed, the app might define additional variables that might have to be set> cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr# build the application on all CPU cores> make -j$(nproc)# now "install" resources into future AppDir> make install DESTDIR=AppDir
AppDir└── AppRun└── your_app.desktop└── your_app.png└── usr ├── bin │ └── your_app ├── lib └── share ├── applications │ └── your_app.desktop └── icons └──└── └── your_app.png
使用 linuxdeploy 打包成 AppImages
# get linuxdeploy's AppImage> wget https://github.com/linuxdeploy/linuxdeploy/releases/download/continuous/linuxdeploy-x86_64.AppImage> chmod +x linuxdeploy-x86_64.AppImage# run linuxdeploy and generate an AppDir> ./linuxdeploy-x86_64.AppImage --appdir AppDir
官方的 cmake 工具打包示例
#! /bin/bashset -xset -e# building in temporary directory to keep system clean# use RAM disk if possible (as in: not building on CI system like Travis, and RAM disk is available)if [ "$CI" == "" ] && [ -d /dev/shm ]; then TEMP_BASE=/dev/shmelse TEMP_BASE=/tmpfiBUILD_DIR=$(mktemp -d -p "$TEMP_BASE" appimage-build-XXXXXX)# make sure to clean up build dir, even if errors occurcleanup () { if [ -d "$BUILD_DIR" ]; then rm -rf "$BUILD_DIR" fi}trap cleanup EXIT# store repo root as variableREPO_ROOT=$(readlink -f $(dirname $(dirname $0)))OLD_CWD=$(readlink -f .)# switch to build dirpushd "$BUILD_DIR"# configure build files with CMake# we need to explicitly set the install prefix, as CMake's default is /usr/local for some reason...cmake "$REPO_ROOT" -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr# build project and install files into AppDirmake -j$(nproc)make install DESTDIR=AppDir# now, build AppImage using linuxdeploy and linuxdeploy-plugin-qt# download linuxdeploy and its Qt pluginwget https://github.com/linuxdeploy/linuxdeploy/releases/download/continuous/linuxdeploy-x86_64.AppImagewget https://github.com/linuxdeploy/linuxdeploy-plugin-qt/releases/download/continuous/linuxdeploy-plugin-qt-x86_64.AppImage# make them executablechmod +x linuxdeploy*.AppImage# make sure Qt plugin finds QML sources so it can deploy the imported filesexport QML_SOURCES_PATHS="$REPO_ROOT"/src# initialize AppDir, bundle shared libraries for QtQuickApp, use Qt plugin to bundle additional resources, and build AppImage, all in one single command./linuxdeploy-x86_64.AppImage --appdir AppDir --plugin qt --output appimage# move built AppImage back into original CWDmv QtQuickApp*.AppImage "$OLD_CWD" 作者: Escape
链接: https://www.escapelife.site/posts/13d44616.html



推荐阅读 点击标题可跳转


转载地址:https://mingongge.blog.csdn.net/article/details/115291138 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
关于作者
