【Android】 Android中Log调试详解
发布日期:2021-06-29 20:55:22
浏览次数:3
分类:技术文章
本文共 14459 字,大约阅读时间需要 48 分钟。
LOG类: public final class Log extends Object java.lang.Object android.util.Log Constants int ASSERT Priority constant for the println method. int DEBUG Priority constant for the println method; use Log.d. 输出DEBUG故障日志信息 int ERROR Priority constant for the println method; use Log.e. 输出ERROR错误日志信息 int INFO Priority constant for the println method; use Log.i. 输出INFO程序日志信息 int VERBOSE Priority constant for the println method; use Log.v. 输出VERBOSE冗余日志信息int WARN Priority constant for the println method; use Log.w. 输出WARN警告日志信息
参考示例:
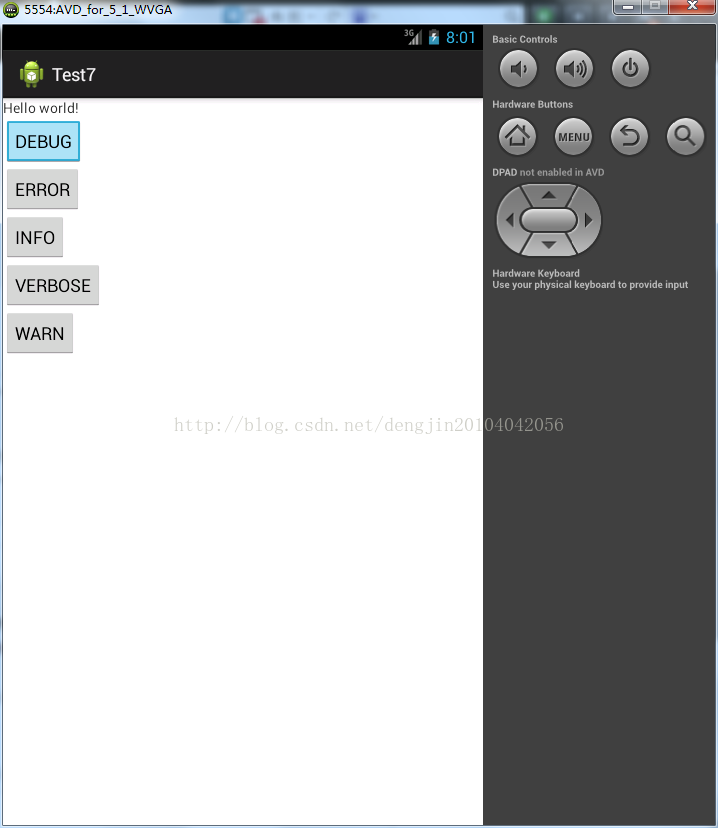
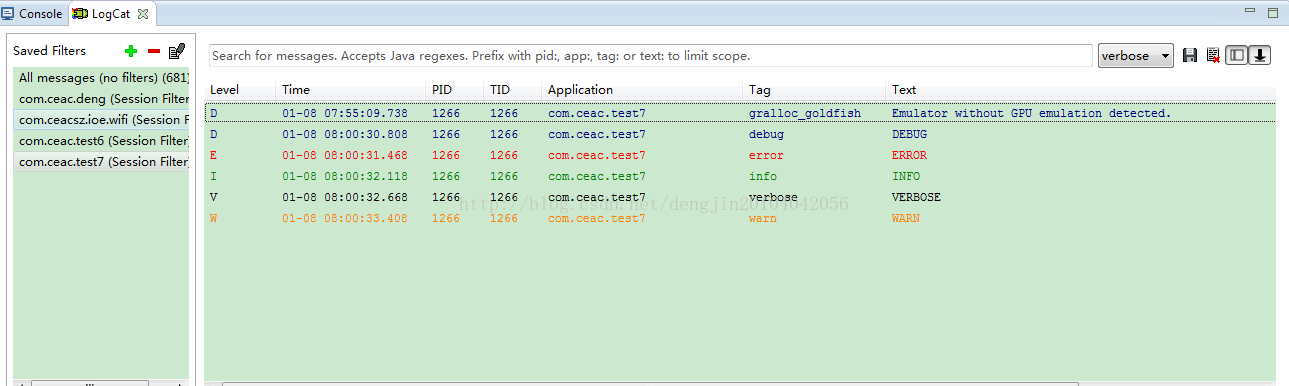
package com.ceac.test7;import android.support.v7.app.ActionBarActivity;import android.os.Bundle;import android.util.Log;import android.view.Menu;import android.view.MenuItem;import android.view.View;import android.view.View.OnClickListener;import android.widget.Button;public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity implements OnClickListener{ private Button button; private Button button2; private Button button3; private Button button4; private Button button5; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); button = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1); button2 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button2); button3 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button3); button4 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button4); button5 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button5); button.setOnClickListener(this); button2.setOnClickListener(this); button3.setOnClickListener(this); button4.setOnClickListener(this); button5.setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View v) { switch (v.getId()) { case R.id.button1: Log.d("debug", "DEBUG"); break; case R.id.button2: Log.e("error", "ERROR"); break; case R.id.button3: Log.i("info", "INFO"); break; case R.id.button4: Log.v("verbose", "VERBOSE"); break; case R.id.button5: Log.w("warn", "WARN"); break; default: break; } }} 运行结果: Android源码详解:
/* * Copyright (C) 2006 The Android Open Source Project * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */package android.util;import com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit;import java.io.PrintWriter;import java.io.StringWriter;import java.net.UnknownHostException;/** * API for sending log output. * *Generally, use the Log.v() Log.d() Log.i() Log.w() and Log.e() * methods. * *
The order in terms of verbosity, from least to most is * ERROR, WARN, INFO, DEBUG, VERBOSE. Verbose should never be compiled * into an application except during development. Debug logs are compiled * in but stripped at runtime. Error, warning and info logs are always kept. * *
Tip: A good convention is to declare a
TAGconstant * in your class: * *private static final String TAG = "MyActivity";* * and use that in subsequent calls to the log methods. * * *Tip: Don't forget that when you make a call like *
Log.v(TAG, "index=" + i);* that when you're building the string to pass into Log.d, the compiler uses a * StringBuilder and at least three allocations occur: the StringBuilder * itself, the buffer, and the String object. Realistically, there is also * another buffer allocation and copy, and even more pressure on the gc. * That means that if your log message is filtered out, you might be doing * significant work and incurring significant overhead. */public final class Log { /** * Priority constant for the println method; use Log.v. */ public static final int VERBOSE = 2; /** * Priority constant for the println method; use Log.d. */ public static final int DEBUG = 3; /** * Priority constant for the println method; use Log.i. */ public static final int INFO = 4; /** * Priority constant for the println method; use Log.w. */ public static final int WARN = 5; /** * Priority constant for the println method; use Log.e. */ public static final int ERROR = 6; /** * Priority constant for the println method. */ public static final int ASSERT = 7; /** * Exception class used to capture a stack trace in {@link #wtf()}. */ private static class TerribleFailure extends Exception { TerribleFailure(String msg, Throwable cause) { super(msg, cause); } } /** * Interface to handle terrible failures from {@link #wtf()}. * * @hide */ public interface TerribleFailureHandler { void onTerribleFailure(String tag, TerribleFailure what); } private static TerribleFailureHandler sWtfHandler = new TerribleFailureHandler() { public void onTerribleFailure(String tag, TerribleFailure what) { RuntimeInit.wtf(tag, what); } }; private Log() { } /** * Send a {@link #VERBOSE} log message. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. */ public static int v(String tag, String msg) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, VERBOSE, tag, msg); } /** * Send a {@link #VERBOSE} log message and log the exception. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. * @param tr An exception to log */ public static int v(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, VERBOSE, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr)); } /** * Send a {@link #DEBUG} log message. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. */ public static int d(String tag, String msg) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, DEBUG, tag, msg); } /** * Send a {@link #DEBUG} log message and log the exception. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. * @param tr An exception to log */ public static int d(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, DEBUG, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr)); } /** * Send an {@link #INFO} log message. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. */ public static int i(String tag, String msg) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, INFO, tag, msg); } /** * Send a {@link #INFO} log message and log the exception. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. * @param tr An exception to log */ public static int i(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, INFO, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr)); } /** * Send a {@link #WARN} log message. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. */ public static int w(String tag, String msg) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, WARN, tag, msg); } /** * Send a {@link #WARN} log message and log the exception. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. * @param tr An exception to log */ public static int w(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, WARN, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr)); } /** * Checks to see whether or not a log for the specified tag is loggable at the specified level. * * The default level of any tag is set to INFO. This means that any level above and including * INFO will be logged. Before you make any calls to a logging method you should check to see * if your tag should be logged. You can change the default level by setting a system property: * 'setprop log.tag.' * Where level is either VERBOSE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, ASSERT, or SUPPRESS. SUPPRESS will * turn off all logging for your tag. You can also create a local.prop file that with the * following in it: * 'log.tag. = ' * and place that in /data/local.prop. * * @param tag The tag to check. * @param level The level to check. * @return Whether or not that this is allowed to be logged. * @throws IllegalArgumentException is thrown if the tag.length() > 23. */ public static native boolean isLoggable(String tag, int level); /* * Send a {@link #WARN} log message and log the exception. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param tr An exception to log */ public static int w(String tag, Throwable tr) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, WARN, tag, getStackTraceString(tr)); } /** * Send an {@link #ERROR} log message. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. */ public static int e(String tag, String msg) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, ERROR, tag, msg); } /** * Send a {@link #ERROR} log message and log the exception. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. * @param tr An exception to log */ public static int e(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, ERROR, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr)); } /** * What a Terrible Failure: Report a condition that should never happen. * The error will always be logged at level ASSERT with the call stack. * Depending on system configuration, a report may be added to the * {@link android.os.DropBoxManager} and/or the process may be terminated * immediately with an error dialog. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. * @param msg The message you would like logged. */ public static int wtf(String tag, String msg) { return wtf(tag, msg, null); } /** * What a Terrible Failure: Report an exception that should never happen. * Similar to {@link #wtf(String, String)}, with an exception to log. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. * @param tr An exception to log. */ public static int wtf(String tag, Throwable tr) { return wtf(tag, tr.getMessage(), tr); } /** * What a Terrible Failure: Report an exception that should never happen. * Similar to {@link #wtf(String, Throwable)}, with a message as well. * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. * @param msg The message you would like logged. * @param tr An exception to log. May be null. */ public static int wtf(String tag, String msg, Throwable tr) { TerribleFailure what = new TerribleFailure(msg, tr); int bytes = println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, ASSERT, tag, msg + '\n' + getStackTraceString(tr)); sWtfHandler.onTerribleFailure(tag, what); return bytes; } /** * Sets the terrible failure handler, for testing. * * @return the old handler * * @hide */ public static TerribleFailureHandler setWtfHandler(TerribleFailureHandler handler) { if (handler == null) { throw new NullPointerException("handler == null"); } TerribleFailureHandler oldHandler = sWtfHandler; sWtfHandler = handler; return oldHandler; } /** * Handy function to get a loggable stack trace from a Throwable * @param tr An exception to log */ public static String getStackTraceString(Throwable tr) { if (tr == null) { return ""; } // This is to reduce the amount of log spew that apps do in the non-error // condition of the network being unavailable. Throwable t = tr; while (t != null) { if (t instanceof UnknownHostException) { return ""; } t = t.getCause(); } StringWriter sw = new StringWriter(); PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(sw); tr.printStackTrace(pw); return sw.toString(); } /** * Low-level logging call. * @param priority The priority/type of this log message * @param tag Used to identify the source of a log message. It usually identifies * the class or activity where the log call occurs. * @param msg The message you would like logged. * @return The number of bytes written. */ public static int println(int priority, String tag, String msg) { return println_native(LOG_ID_MAIN, priority, tag, msg); } /** @hide */ public static final int LOG_ID_MAIN = 0; /** @hide */ public static final int LOG_ID_RADIO = 1; /** @hide */ public static final int LOG_ID_EVENTS = 2; /** @hide */ public static final int LOG_ID_SYSTEM = 3; /** @hide */ public static native int println_native(int bufID, int priority, String tag, String msg);}
转载地址:https://dengjin.blog.csdn.net/article/details/42526067 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
路过,博主的博客真漂亮。。
[***.116.15.85]2024年04月13日 04时59分25秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
分布式系统:Primary Backup - 故障容忍的虚拟机
2019-04-30
分布式系统:raft
2019-04-30
分布式系统:Raft(实验作业2A)
2019-04-30
分布式系统:Raft(实验作业2B)
2019-04-30
分布式系统:Raft(实验作业2C)
2019-04-30
一微秒的差别
2019-04-30
分布式系统:Raft(实验作业3A)
2019-04-30
分布式系统 Spinnaker
2019-04-30
分布式系统 Lab3B KVRaft snapshot
2019-04-30
分布式系统 Zookeeper
2019-04-30
分布式系统:Lec 10 分布式事务
2019-04-30
分布式系统:FaRM
2019-04-30
分布式系统:ZooKeeper 基本用例
2019-04-30
分布式系统:Spark
2019-04-30
分布式系统:Naiad
2019-04-30
分布式系统:参数服务器
2019-04-30
分布式系统:FastRPC eRPC
2019-04-30
奇异值分解简要笔记
2019-04-30
6.824(2020年) Lab1 MapReduce
2019-04-30