
Java语言入门(五)——面向对象(二)
发布日期:2022-02-28 07:22:48
浏览次数:26
分类:技术文章
本文共 6531 字,大约阅读时间需要 21 分钟。
Java语言入门
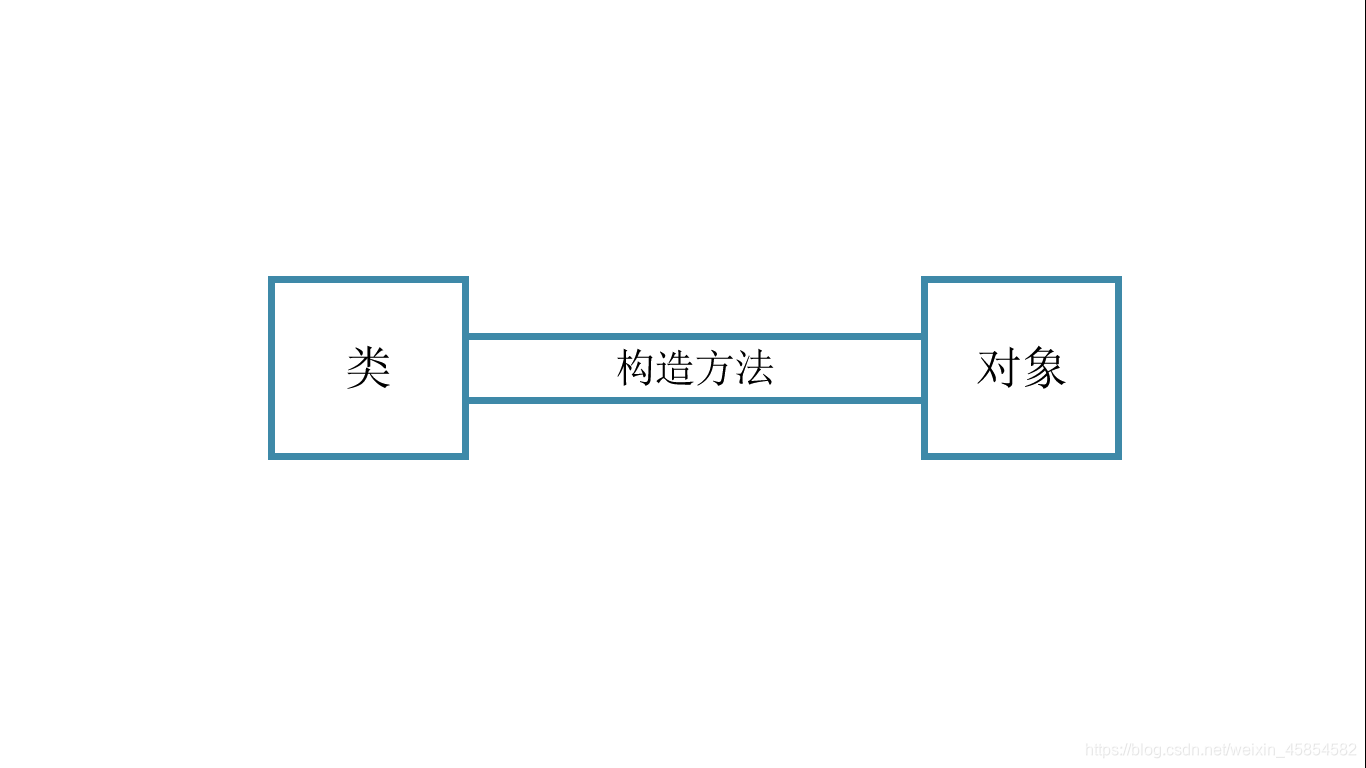
类、对象、构造方法关系图

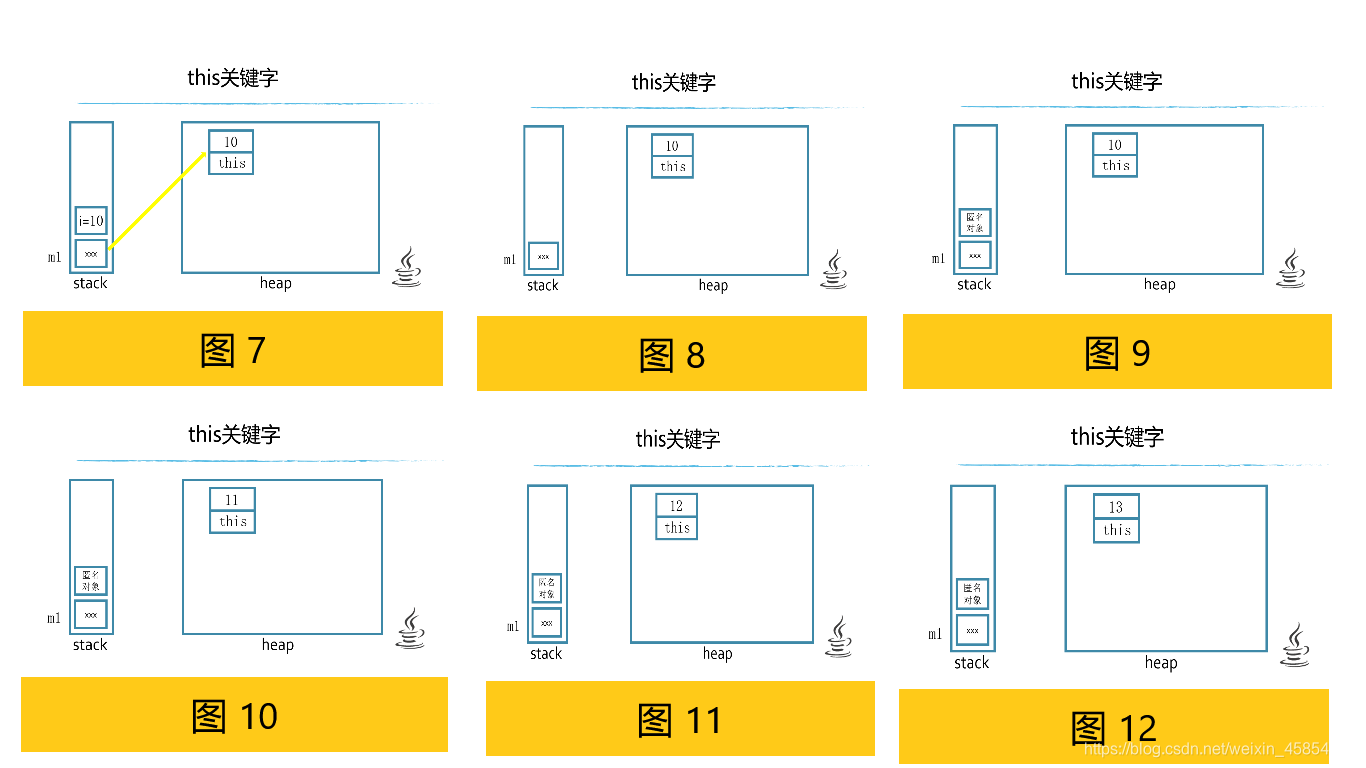
class Money{ int i=5; public Money() { } public Money(int i) //构造方法, i为局部变量 { this.i=i; } //第一个i为局部变量,第二个i为成员变量 public Money add() //成员方法,返回值是对象 { i++; //i为成员变量 return this;} void print() { System.out.println(i);}} class Test-5.1{ public static void main(String[] args) { Money m1=new Money(10); m1.add().add().add().print();} //13} 垃圾回收机制
1 c++中的析构方法
2 java中的finalize()方法 3 System.gc的作用class Rubbish{ public void finalize() { System.out.println("rubbish is over!"); } public static void main(String[] args) { new Rubbish(); new Rubbish(); //new Rubbish().finalize(); System.gc(); }} 参数传递
1 基本数据类型的参数传递
class Test-5.2{ public static void main(String[] args) { int x=10; change(x); System.out.println(x); //10 } static void change(int x) { x+=15; }} 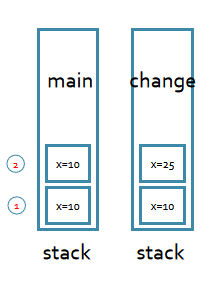
class PP{ int x=0; //成员变量在堆内存 public static void main(String[] args) { int x=10; //局部变量在栈内存 change(new PP()); System.out.println(x); //10 //System.out.println(this.x); } static void change(PP y) { y.x=15;}} 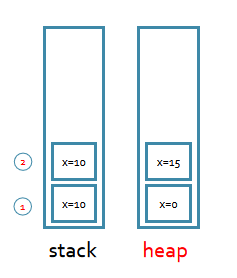
class TT{ int x=0; public static void main(String[] args) { int x=10; TT t=new TT(); change(t); System.out.println(t.x); //15 } static void change(TT y) //引用传递 { y.x=15; } } 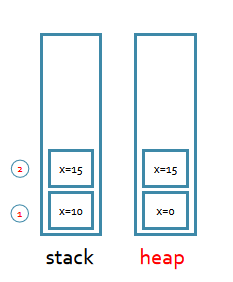
static关键字
1 静态变量,放在data seg,公共的属性,在内存中有且只有一份,又称为类变量,不用生成对象。
2 静态方法,也可以不用生成对象,用类名直接调用,静态方法只能调用静态方法或变量,非静态方法可访问静态方法或变量,这是因为,对于非静态的方法和变量,需要先创建类的实例对象后才可使用,而静态方法在使用前不用创建任何实例对象。class Student{ String name; static String school="GY"; public Student(String name) { this.name=name; } void print() { System.out.println(this.name+":"+school); }}class Test-5.3{ public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1=new Student("huang"); Student s2=new Student("wang"); Student.school="GYD"; //也可用s1.school="GYD";一改全改 s1.print(); //huang:GYD s2.print();} //wang:GYD} 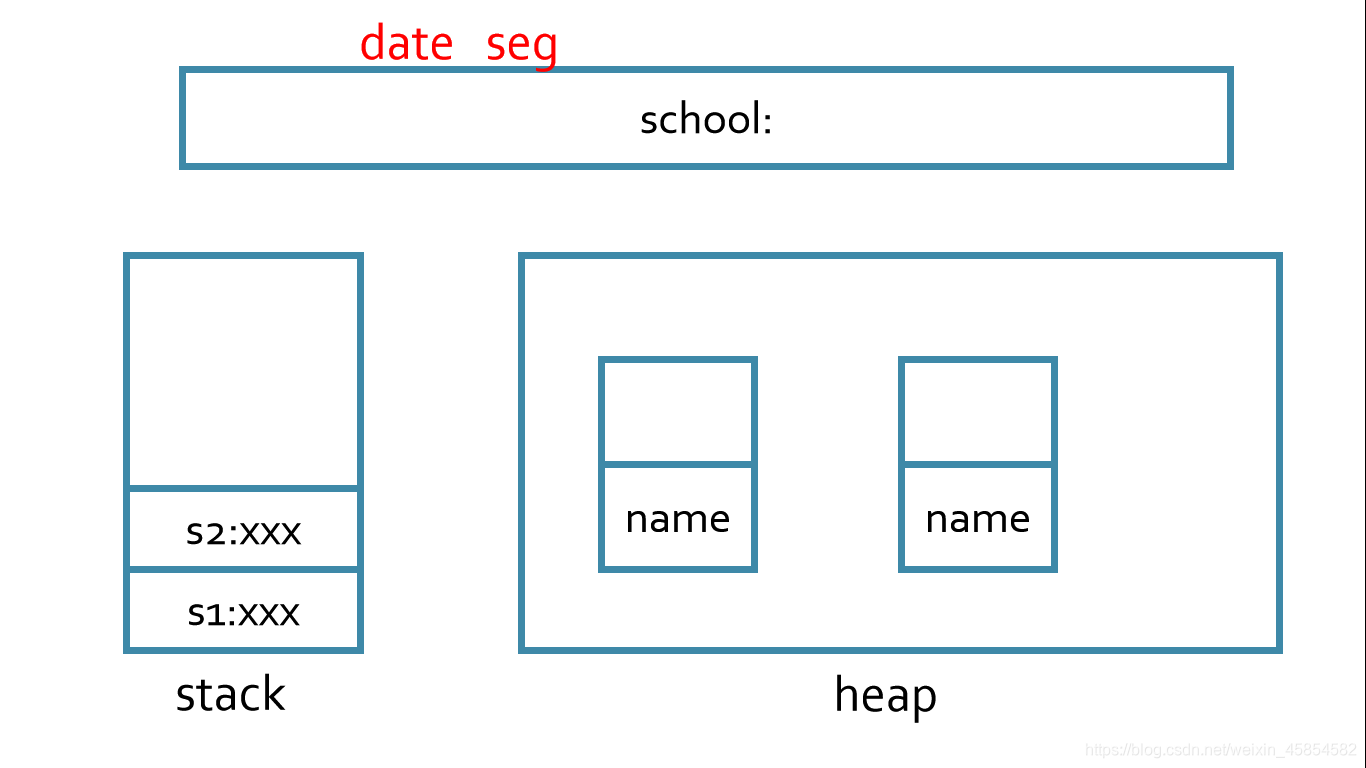
class Student{ String name; static String school;}class Test-5.4{ public static void main(String[] args) { Student.school="GYD"; }} class Student{ String name; static String school; void ch1() //非静态的方法可以访问静态的变量 { System.out.println(school); } static void ch2() //静态方法可以访问静态的变量 { System.out.println(school); //name="huang";错误,普通变量必须生成对象}}class Test-5.5{ public static void main(String[] args) { Student.school="GYD"; new Student().ch1(); //GYD new Student().ch2(); //GYD }} class HH{ public static void main(String[] args) { int x=10; /*new HH().change(x);*/ change(x); System.out.println(x); //10} static void change(int y) //引用传递,必须为static { y=15; } /*void change(int y) {y=15;} 不加static则需新建对象后再调用*/} class Test-5.6{ public static void main(String[] args) { int x=10; System.out.println(args[0]); //LL System.out.println(args[1]); //JJ SS }}//命令行参数,执行时为java Test-5.6 LL “JJ SS” static的应用
1 统计对象
2 类的单态(例)设计模式 a.构造方法私有 private b.生成静态的对象 c.在类的外部调用该类的某个静态方法以返回类内部创建的对象单态设计模式
class Person{ String name; int x=0; public Person() { ++x; } public void print() { System.out.println(x); }}class Test-5.7{ public static void main(String[] args) { new Person().print(); //1 new Person().print(); //1 new Person().print(); //1 }} class Person{ String name; static int x=0; public Person() { ++x; } public void print() { System.out.println(x); }}class Test-5.8{ public static void main(String[] args) { new Person().print(); //1 new Person().print(); //2 new Person().print(); //3 }} class Person{ String name; static int x=0; static Person p=new Person(); //b /*最好为private static Person p=new Person();*/ private Person() { ++x; } //a public static Person getP() //c { return p; } }class Test-5.9{ public static void main(String[] args) { Person p=Person.getP(); Person p1=Person.getP(); Person p2=Person.getP(); System.out.println(p==p1); //true System.out.println(p1==p2);} //true} //无论生成多少对象,内存中仅有一个对象 String类型
1 两种实例化: (1)直接赋值 ; (2)通过构造方法赋值
区别:内存变化不一样。 一个字符串常量就是一个String的匿名对象。一个字符串赋值后,内容不能改变,只能改变引用。 2 两种比较方式:== 和 equals() 和 compareTo (- 0 +) 3 字符串与字节转化(byte单位小于char) (byte) public String(byte[] bytes) 4 字符串与字符的转换 public String(char[] value) public String(char[] value,int offset,int count) //offset起始点,count数量 public charAt(int index) public char[] toCharArray()//转化成字符数组 5 字符串的操作:截取一部分字符串 public String substring(int beginIndex)字符串池
class Test-5.10{ public static void main(String[] args) { String n1="huang"; //直接赋值,直接入池 String n4="huang"; String n2=new String(“huang”);//构造方法 String n3=new String("huang"); String n5=new String("huang").intern();//入池操作 String n6=new String("huang").intern(); System.out.println(n1==n2); //false System.out.println(n2==n3); //false System.out.println(n1==n4); //true System.out.println(n6==n5); //true System.out.println(n1==n5);} //true} 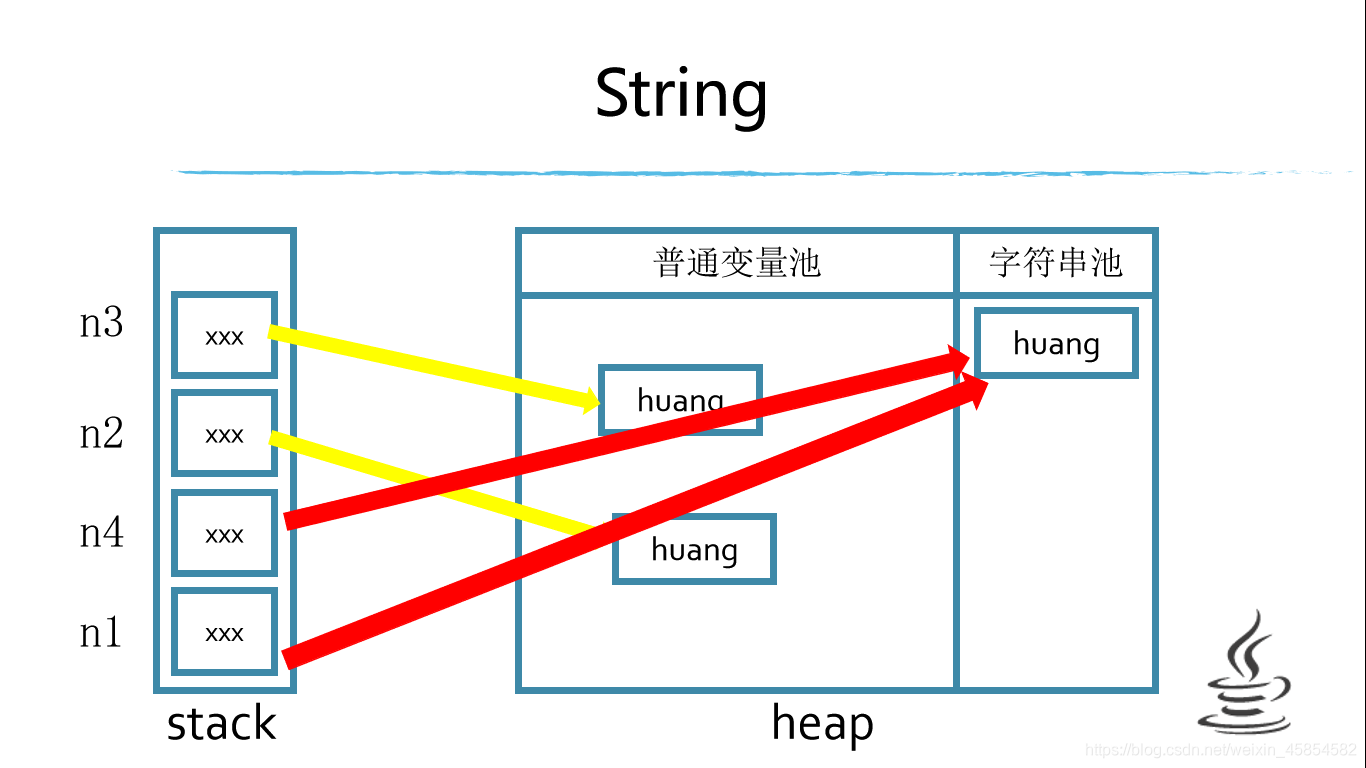
常用String方法
class Test-5.11{ public static void main(String[] args) { String n="huang"; n+="guo"; //改变引用,不要用在循环里面,处理慢 System.out.println(n); }}//(问:字符串改变了吗?有几个对象?)//答:没有改变字符串,改变的只是引用;有3个对象 class Test-5.12{ public static void main(String[] args) { //if(args[0].equals("huang")) if("huang".equals(args[0])//字符串常量与字符串变量比较,应用字符串常量与变量比较,保证比较的正常运行 System.out.println("OK"); else System.out.println("BU OK"); }}//最好采用别的键盘输入方式 class Test-5.14{ public static void main(String[] args) { String n="huang"; char []a=n.toCharArray();//转化成一个个字符 for(char x:a) { System.out.println(x); }//此处用较强for循环是不好的,用普通for循环即可 //h u a n g String h=new String(a,1,2); System.out.println(h); //ua System.out.println(n.charAt(2)); }//a,打印字符串的第几个索引(0-h,1-u,2-a,3-n,4-g) //a} class Test-5.15{ public static void main(String[] args) { String n="huang"; System.out.println(n.substring(0)); //huang System.out.println(n.subString(2)); //ang System.out.println(n.subString(2,3)); //a }} 转载地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_45854582/article/details/105895479 如侵犯您的版权,请留言回复原文章的地址,我们会给您删除此文章,给您带来不便请您谅解!
发表评论
最新留言
感谢大佬
[***.8.128.20]2024年03月30日 04时01分00秒
关于作者

喝酒易醉,品茶养心,人生如梦,品茶悟道,何以解忧?唯有杜康!
-- 愿君每日到此一游!
推荐文章
006_关于变量定义的状态
2019-04-27
007_shell中把变量重置为null
2019-04-27
008_shell创建只读量
2019-04-27
009_shell中从标准输入信息
2019-04-27
010_bash脚本的参数传递
2019-04-27
011_命令行参数的左移
2019-04-27
012_bash中的if判断条件
2019-04-27
013_bash中的加法
2019-04-27
014_bash中的for循环
2019-04-27
015_Arduino上实现一个简单的番茄时钟
2019-04-27
021_Excel的条件格式
2019-04-27
022_Excel空白值批量填充默认值
2019-04-27
023_emacs git-gutter+报错解决
2019-04-27
024_spacemacs支持org-pomodoro的声音提示
2019-04-27
025_everything搜索使用体验
2019-04-27
026_好用的windows小工具clover
2019-04-27
027-Mac触摸板实现窗口移动
2019-04-27
028_AUTOSAR RTE学习笔记-1
2019-04-27
029_AUTOSAR VFB学习笔记-2
2019-04-27
030_AUTOSAR软件组件学习笔记
2019-04-27